Jason
How to powerlifting
Are you looking to take your strength to new heights? Have you considered the incredible benefits of powerlifting? Whether you’re a fitness enthusiast or simply looking to enhance your lifting routine, powerlifting can be the game-changer you’ve been searching for.
But what exactly is powerlifting, and how can it help you boost your strength? In this article, I will guide you through essential tips and techniques that will maximize your powerlifting potential and help you achieve your strength goals.
Key Takeaways:
- Powerlifting is a training method that focuses on enhancing overall strength.
- Proper form and technique are crucial for maximizing powerlifting gains.
- Core strength is essential for stability and efficient force transfer.
- Powerlifting exercises like squats, bench press, and deadlifts target major muscle groups.
- Exploring advanced powerlifting techniques can further challenge and elevate your strength.
Understanding Powerlifting
Before diving into the specifics of powerlifting, it’s important to understand what powerlifting actually entails. Powerlifting is a strength sport that focuses on three main lifts: the squat, bench press, and deadlift. Unlike other forms of lifting routines, powerlifting prioritizes maximum strength and performance in these three lifts rather than overall muscle development or aesthetics.
In powerlifting, the objective is to lift as much weight as possible in each of the three lifts. Competitors are judged based on the maximum weight successfully lifted, and each lift is performed for a single repetition with proper form and technique. Powerlifting emphasizes full-body strength and requires a combination of muscular power, stability, and mental focus.
“Powerlifting is not just about physical strength; it’s a mental and emotional journey as well. It pushes you to surpass your limits and continuously strive for improvement.” – Mark Bell, professional powerlifter
Unlike bodybuilding or weightlifting, powerlifting does not focus on the number of repetitions performed or muscle isolation exercises. Powerlifters typically follow a structured training program that includes specific exercises to improve their technique, increase strength, and optimize performance in the squat, bench press, and deadlift. The goal is to progressively lift heavier weights over time, breaking personal records and pushing the boundaries of strength.
The Benefits of Powerlifting
Powerlifting offers numerous benefits for individuals looking to enhance their strength and overall fitness. Here are some key advantages of incorporating powerlifting into your lifting routine:
- Increased overall strength: Powerlifting exercises target multiple muscle groups, leading to significant increases in overall strength and power.
- Improved bone density: The heavyweight lifting involved in powerlifting helps stimulate bone growth and increase bone density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis.
- Enhanced athletic performance: The explosive movements and full-body engagement in powerlifting can improve athletic performance in various sports and activities.
- Boosted metabolism: Powerlifting workouts stimulate muscle growth, which can increase your resting metabolic rate and support weight loss efforts.
- Mental resilience: Powerlifting challenges your mental toughness, discipline, and perseverance, fostering resilience that carries over into other areas of your life.
In conclusion, understanding the foundations of powerlifting is crucial to maximizing your potential in the gym. By focusing on the squat, bench press, and deadlift and following a structured training program, you can build impressive strength and achieve your powerlifting goals.
| Powerlifting Exercises | Muscle Groups Targeted |
|---|---|
| Squat | Quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, core |
| Bench Press | Chest, shoulders, triceps |
| Deadlift | Back, glutes, hamstrings, core |
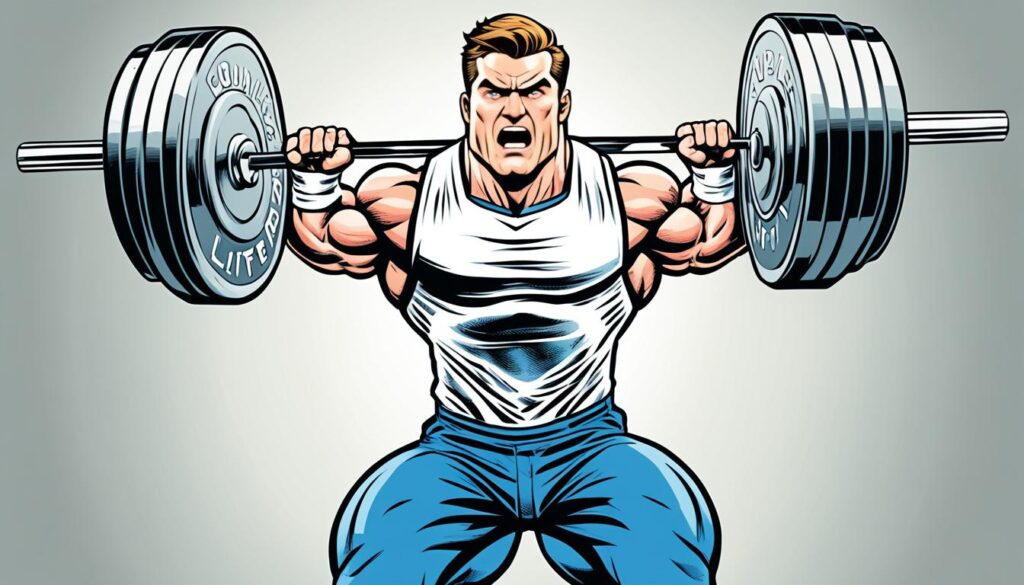
Proper Form for Squats
Squats are a fundamental exercise in powerlifting that target the lower body. Mastering the proper form is crucial to prevent injuries and maximize strength gains. In this section, I will guide you through the correct positioning, breathing techniques, and common mistakes to avoid when performing squats.
Correct Positioning
When performing squats, it’s important to have proper positioning to ensure maximum effectiveness and safety. Here are the key steps to follow:
- Start by standing with your feet shoulder-width apart and toes slightly turned outward.
- Place the barbell on your upper back, resting it across your traps.
- Engage your core and maintain a straight back throughout the entire movement.
- Lower your body by bending at the knees and hips, keeping your chest up and eyes forward.
- Go down until your thighs are parallel to the ground or slightly below, maintaining control of the movement.
- Drive through your heels to stand back up, extending your hips and knees simultaneously.
Remember to always maintain proper form and avoid rounding your back or letting your knees collapse inward. Engaging your core and keeping your chest up will help maintain stability and reduce the risk of injury.
Breathing Techniques
Breathing plays a crucial role in squats as it helps stabilize your core and provides support during the exercise. Follow these breathing techniques to optimize your performance:
- Take a deep breath before initiating the squat movement.
- Hold your breath as you descend into the squat position.
- Exhale forcefully as you drive through your heels to stand back up.
- Repeat this breathing pattern for each repetition, ensuring proper breath control throughout the set.
Proper breathing will help you maintain stability, increase intra-abdominal pressure, and enhance overall performance during squats.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
It’s important to be aware of common mistakes that can hinder your squat performance. Avoid these errors to ensure optimal results:
“Squats are a cornerstone exercise in powerlifting, targeting the lower body. Mastering proper form, positioning, and breathing techniques will maximize strength gains and prevent injuries.” – Certified Powerlifting Coach, Sarah Thompson
- Avoid letting your knees collapse inward. Instead, focus on pushing your knees out and tracking them in line with your toes.
- Don’t round your back or let it collapse forward. Maintain a neutral spine throughout the entire movement.
- Avoid excessive forward lean. Keep your chest up and maintain an upright position as you squat.
- Don’t rush the movement. Maintain control throughout the entire range of motion.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you’ll be able to perform squats with proper form, reducing the risk of injury and maximizing the benefits of this essential powerlifting exercise.
| Common Mistake | Correct Form |
|---|---|
| Knees collapsing inward | Push knees out, tracking in line with toes |
| Rounded back | Maintain a neutral spine throughout |
| Excessive forward lean | Keep chest up, maintain an upright position |
| Rushing the movement | Maintain control throughout the entire range of motion |
Mastering the proper form for squats is essential for any powerlifting routine. By following the correct positioning, breathing techniques, and avoiding common mistakes, you’ll be able to maximize your strength gains and reduce the risk of injury. Incorporate squats into your lifting routine and experience the benefits of this powerful lower body exercise.
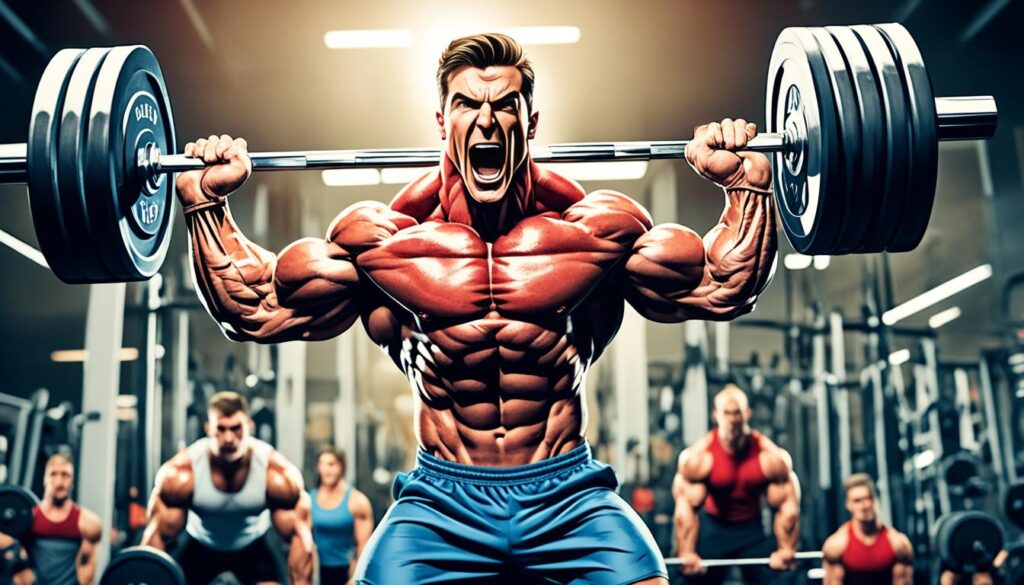
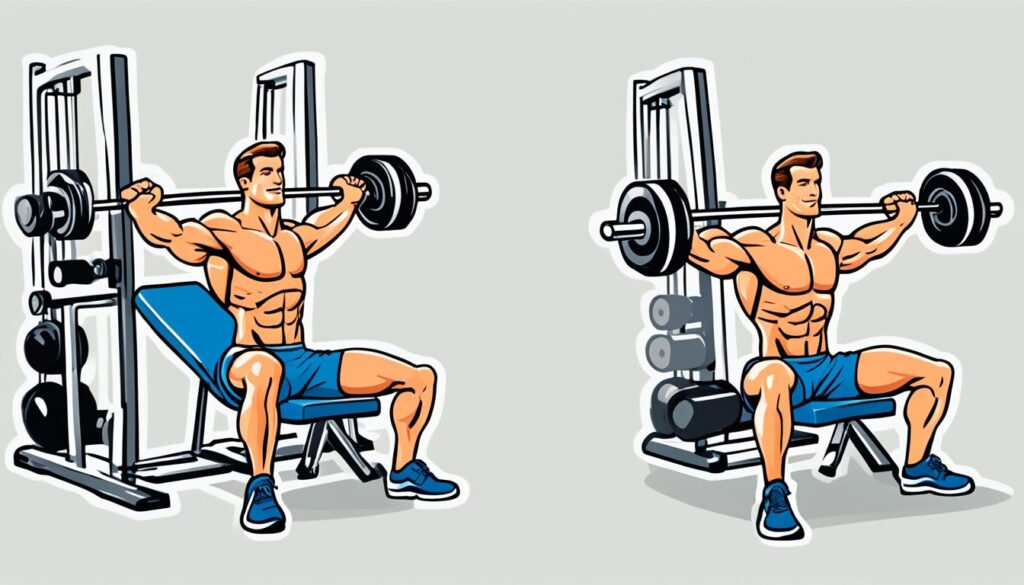
Bench Press Technique
The bench press is a classic powerlifting exercise that targets the upper body, specifically the chest, shoulders, and triceps. Mastering the bench press technique is essential for lifting heavier weights and developing a stronger upper body in your lifting routine.
When performing the bench press, pay attention to the following key elements:
- Grip Width: Position your hands slightly wider than shoulder-width apart on the barbell. This grip allows for optimal engagement of the chest muscles and stability during the lift.
- Body Positioning: Lie flat on the bench with your feet firmly planted on the floor. Create a slight arch in your lower back and ensure your shoulder blades are retracted and in contact with the bench.
- Execution: Lower the barbell slowly and under control to your mid-chest while keeping your elbows at a 45-degree angle. Pause for a brief moment and then push the barbell back up in a controlled manner, fully extending your arms. Remember to exhale during the exertion phase of the lift.
By focusing on proper grip width, body positioning, and execution, you will not only enhance your bench press performance but also minimize the risk of injury. As you progress, gradually increase the weight and challenge your muscles to continuously adapt and grow.
Remember, consistency and gradual progression are key to improving your bench press and upper body strength. Don’t be discouraged if you can’t lift heavy weights right away – strength takes time to build. Keep practicing the correct technique, and over time, you’ll see significant improvements in your lifting routine.
Now that you have a solid understanding of the bench press technique, let’s move onto the next section where we will explore another essential powerlifting exercise – deadlifts for strength.
Deadlifts for Strength
When it comes to powerlifting exercises, deadlifts reign as the king. They engage multiple muscle groups and hold the key to overall strength development. In this section, I will guide you through the proper form for deadlifts, ensuring that you maximize your strength gains.
One crucial aspect of deadlifts is grip variation. Experiment with different grip styles, such as the overhand grip, mixed grip, or hook grip, to find the one that feels most comfortable and secure for you. The right grip will provide stability and confidence as you lift heavier weights.
The starting position is also vital in deadlifts. Begin by standing with your feet shoulder-width apart, toes pointing slightly outward. Position the barbell directly above the middle of your feet. Bend your knees and hips, keeping your spine neutral, and reach down to grasp the bar with your chosen grip.
Now, it’s time to unleash the power of your hips. As you lift the barbell, focus on initiating the movement by driving your hips forward, pushing through your heels. Maintain a straight back throughout the lift, ensuring proper spinal alignment.
To solidify your deadlift technique and build strength, regularly integrate this powerlifting exercise into your lifting routine. As you progress, gradually increase the weight, pushing yourself to new limits.
Benefits of Deadlifts:
- Enhanced overall strength and power.
- Improved grip strength.
- Increased muscle mass in the posterior chain, including the glutes, hamstrings, and back.
- Engagement of the core for stability and balance.
- Improved posture and spinal erector strength.
By mastering the proper form for deadlifts and consistently integrating them into your powerlifting routine, you’ll experience substantial gains in strength and performance. Let’s embrace the challenge and unlock your true powerlifting potential.
Quoting a Pro Powerlifter:
“Deadlifts are the ultimate display of raw strength and power. By incorporating this exercise into your lifting routine, you’ll witness incredible physical and mental transformations. Stay disciplined, focus on form, and unleash your inner beast!” – Mark Stevens, Professional Powerlifter
The Importance of Core Strength
Core strength is a crucial element in the world of powerlifting. The core muscles, which include the abs, lower back, and glutes, act as a stable foundation for every movement you perform during a powerlifting routine. Not only does a strong core enhance your overall powerlifting lifts, but it also plays a significant role in reducing the risk of injuries.
When you have a solid core, you provide stability and support for your entire body, allowing for efficient force transfer from your lower body to your upper body and vice versa. This transfer of force is vital in powerlifting as it increases your lifting capacity and enables you to generate more power.
Additionally, a strong core helps you maintain proper form and technique throughout your lifts, preventing any unnecessary strain on other muscle groups. It acts as a stabilizer, ensuring that your body stays balanced and aligned, reducing the risk of injuries that may occur due to poor stability or improper weight distribution.
To strengthen your core for powerlifting, it’s essential to incorporate specific exercises and strategies into your training routine. These exercises can include planks, Russian twists, hanging leg raises, and weighted decline sit-ups. By targeting and strengthening your core muscles, you’ll not only improve your powerlifting performance but also enhance your overall athletic abilities and functional strength.
Benefits of Core Strength in Powerlifting:
- Enhanced stability: A strong core provides a solid foundation, enhancing stability during powerlifting movements.
- Increased lifting capacity: Efficient force transfer through a strong core allows you to lift heavier weights.
- Improved technique: A stable core helps you maintain proper form and technique throughout your lifts, reducing the risk of injuries.
- Enhanced overall strength: Strengthening your core muscles contributes to greater overall strength and power.
By focusing on strengthening your core, you’ll unlock your true powerlifting potential and take your performance to the next level. Remember that core strength is not just about aesthetics; it’s the foundation that supports your powerlifting goals.
Advanced Techniques in Powerlifting
Once you have mastered the foundational techniques of powerlifting, you may be ready to explore more advanced movements and take your training to new heights. In this section, I will introduce you to two advanced powerlifting exercises: the thrust and the snatch.
The Thrust
The thrust is an explosive and dynamic movement that targets multiple muscle groups, including the legs, core, and shoulders. It is a compound exercise that combines elements of the squat and overhead press. To perform a thrust, follow these steps:
- Start by standing with your feet shoulder-width apart, holding a barbell at shoulder height with an overhand grip.
- Bend your knees and lower into a deep squat position.
- Drive through your heels as you explosively extend your legs and hips, propelling the barbell overhead.
- Lock out your arms at the top of the movement and hold for a second.
- Lower the barbell back down to shoulder height and repeat for the desired number of reps.
The thrust is a challenging exercise that requires both strength and coordination. It can help improve your powerlifting performance by developing explosive power and enhancing your overall athleticism.
The Snatch
The snatch is an Olympic-style lift that requires speed, precision, and technique. It targets the entire body, including the legs, back, shoulders, and arms. The snatch involves lifting a barbell from the ground to an overhead position in one fluid motion. Here’s a breakdown of the snatch technique:
- Start with the barbell on the ground, positioned slightly in front of your shins.
- Grasp the barbell with a wide grip, palms facing down.
- Lower into a squat position, keeping your back straight and chest up.
- Explosively extend your hips, knees, and ankles, while simultaneously pulling the barbell upwards with your arms.
- As the barbell reaches chest height, quickly drop into a deep squat and catch the barbell overhead with locked arms.
- Stand up from the squat position, maintaining control of the barbell.
- Lower the barbell back down to the starting position and repeat.
The snatch requires a high level of technique and mobility. It challenges your strength, power, and flexibility, making it an excellent exercise to incorporate into your powerlifting routine for overall athletic development.
Remember to start light and gradually increase the weight as you become more comfortable with these advanced techniques. Additionally, seek assistance from a qualified coach or trainer to ensure proper form and avoid injuries.

By incorporating advanced techniques like the thrust and snatch into your powerlifting routine, you can continue to challenge your body, stimulate muscle growth, and push yourself to new heights of strength and performance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, powerlifting is a powerful way to boost your overall strength and improve your lifting routine. By learning and implementing proper form for squats, bench press, and deadlifts, as well as focusing on core strength and exploring advanced techniques, you can elevate your powerlifting performance and achieve your strength goals. Start incorporating these tips into your training sessions and witness the progress firsthand.
FAQ
What is powerlifting?
Powerlifting is a strength sport that focuses on three main lifts: squats, bench press, and deadlifts. It involves lifting heavy weights to test and improve overall strength and power.
Why is powerlifting different from other lifting routines?
Powerlifting is different from other lifting routines because it prioritizes maximum strength in specific lifts, whereas other routines may focus on muscle building or endurance. Powerlifting competitions also have specific rules and equipment requirements.
What is the proper form for squats?
To perform squats with proper form, start with your feet shoulder-width apart, lower your body by bending your knees and hips as if you’re sitting back into a chair, and then push through your heels to stand up straight. Keep your chest up and maintain a neutral spine throughout the movement.
How can I improve my bench press technique?
To improve your bench press technique, ensure that your feet are planted firmly on the ground, grip the bar with your hands slightly wider than shoulder-width apart, lower the bar down to your chest while maintaining control, and then press it back up. Focus on engaging your chest muscles and using proper breathing techniques.
What is the proper deadlift form?
The proper deadlift form involves standing with your feet hip-width apart, gripping the barbell with your hands shoulder-width apart, and keeping your back straight as you hinge from your hips to lower the weight down. Engage your glutes and hamstrings to lift the weight back up, making sure to maintain a neutral spine throughout the movement.
Why is core strength important in powerlifting?
Core strength is vital in powerlifting as it provides stability and helps transfer force effectively from the lower body to the upper body. A strong core also helps maintain proper form during heavy lifts, reducing the risk of injuries and maximizing power output.
What are some advanced techniques in powerlifting?
Some advanced techniques in powerlifting include exercises like thrusters and snatches. Thrusters combine squats and overhead presses, while snatches involve lifting a barbell from the ground to an overhead position in a swift motion. These movements challenge your coordination and increase the intensity of your powerlifting routine.
How can powerlifting improve my overall strength?
Powerlifting focuses on heavy lifts that recruit multiple muscle groups, which leads to increases in overall strength. By regularly incorporating powerlifting exercises into your routine and progressively increasing the weights you lift, you can continually challenge your muscles and stimulate strength gains.
Mastering close grip bench press
Are you struggling to maximize your upper body strength? Looking to refine your tricep development for better performance? Look no further than the close grip bench press. This underrated exercise could be the game-changer you’ve been searching for.
Key Takeaways:
- Close grip bench press is a highly effective exercise for targeting the triceps, chest, and shoulders.
- Mastering the proper technique is essential for maximizing the benefits of this exercise.
- This exercise offers a range of benefits, including improved upper body strength and tricep development.
- Experimenting with close grip bench press variations can add variety and challenge to your training routine.
- Comparing close grip bench press to the traditional bench press can help you determine which exercise is best for you.
With its focus on the triceps, chest, and shoulders, the close grip bench press deserves a spot in your workout routine. This powerful exercise not only strengthens your upper body but also helps you achieve a sculpted and defined physique.
In section 2 of this article, I will guide you through the correct form and technique for performing the close grip bench press. We’ll explore the nuances of this exercise and how to optimize your results.
The close grip bench press technique
When it comes to perfecting your upper body strength and targeting specific muscle groups, mastering the close grip bench press technique is essential. This exercise focuses on the triceps, chest, and shoulders, helping you build overall upper body power and stability.
Performing the close grip bench press with proper form and technique ensures that you maximize its benefits and minimize the risk of injury. Here, I will guide you through the correct execution of this exercise, step by step, to help you achieve optimal results.
- Start by lying flat on a bench, positioning your feet firmly on the ground for stability.
- Grip the barbell with a narrow grip, placing your hands slightly closer than shoulder-width apart.
- Engage your core and maintain a neutral spine throughout the exercise.
- Lower the barbell slowly and under control toward your chest, keeping your elbows tucked close to your body.
- Pause when the barbell touches your chest, and then push it back up to the starting position, fully extending your arms.
- Repeat for the desired number of repetitions, focusing on maintaining proper form throughout.
Remember to breathe steadily throughout the movement, inhaling as you lower the barbell and exhaling forcefully as you push it back up. Keeping a controlled tempo and focusing on the mind-muscle connection will help you engage the targeted muscle groups effectively.
Check out the visual representation of the close grip bench press technique below:
If you’re unsure about your form or have any concerns, consider seeking guidance from a qualified fitness professional to ensure that you perform the close grip bench press correctly and safely.
Tip: The close grip bench press can be a challenging exercise, especially if you’re new to it. Start with lighter weights and gradually increase the resistance as your strength and technique improve.
By following the proper close grip bench press technique, you’ll be on your way to developing stronger triceps, a more defined chest, and powerful shoulders. Now that you have a solid foundation of the exercise, let’s explore the incredible benefits it can offer in the next section.
Benefits of close grip bench press
Incorporating close grip bench press into your workout routine offers a multitude of benefits for athletes and fitness enthusiasts. This exercise targets the triceps and upper body muscles, allowing you to build strength, increase pushing power, and sculpt defined muscles.
Here are some key advantages of including close grip bench press in your training:
- Tricep Strength: Close grip bench press specifically targets the triceps, helping to develop and strengthen these muscles. By engaging the triceps effectively, you can improve your overall upper body strength and enhance your performance in other exercises.
- Increased Pushing Power: By engaging the triceps, chest, and shoulders, close grip bench press helps to build pushing power. This increase in strength and power can be beneficial for sports that involve pushing movements, such as football, basketball, and martial arts.
- Improved Upper Body Definition: Close grip bench press allows you to sculpt and define your tricep muscles, creating a more aesthetically pleasing upper body physique. Consistent training with this exercise can help you achieve the toned and muscular look you desire.
- Versatility: Close grip bench press can be easily incorporated into various training programs and routines. Whether you’re a beginner or an advanced lifter, you can adapt this exercise by adjusting the intensity, volume, and weight to match your fitness level and goals.
- Functional Strength: The close grip bench press exercise mimics pushing movements commonly performed in daily activities, such as pushing a heavy door or lifting objects. By strengthening and training these muscles, you can improve your overall functional strength and make everyday tasks easier.
“Incorporating close grip bench press into your workout routine can provide numerous benefits, including increased tricep strength, improved pushing power, and enhanced upper body definition.”
By combining these benefits with a well-rounded training program that includes a variety of exercises, you can optimize your strength gains and overall fitness.
As with any exercise, it’s essential to perform close grip bench press with proper form and technique to minimize the risk of injury and maximize results. Always consult with a qualified fitness professional or trainer if you’re new to this exercise or have any concerns.
Enhancing tricep development
When it comes to targeting and developing your triceps, the close grip bench press is a highly effective exercise. By incorporating this compound movement into your training regimen, you can sculpt and strengthen your tricep muscles for improved performance.
The close grip bench press specifically targets the triceps, making it an ideal exercise for tricep development. This variation of the traditional bench press involves bringing your hands closer together on the barbell, which places more emphasis on the tricep muscles.
Performing the close grip bench press with proper form is crucial to maximize tricep activation and prevent injury. To ensure you are doing it correctly:
- Start by lying on a flat bench with your feet planted firmly on the ground.
- Grasp the barbell with a grip slightly narrower than shoulder-width apart, keeping your elbows close to your body.
- Lower the barbell to your mid-chest, maintaining control throughout the movement.
- Press the barbell back up to the starting position, fully extending your arms.
Remember to engage your core and maintain a stable body position throughout the exercise. It’s also essential to use an appropriate weight that allows you to perform the exercise with proper form and the intended muscle engagement.
Adding the close grip bench press to your routine can be beneficial for both beginners and advanced lifters. It not only helps to build tricep strength but also contributes to overall upper body development.
By incorporating the close grip bench press into your workout routine, you can take your tricep development to the next level. Remember to progressively overload your triceps by gradually increasing the weight or number of repetitions as you become stronger.
Keep in mind that while the close grip bench press is an excellent exercise for tricep development, it should be complemented by a well-rounded training program that includes a variety of exercises targeting different muscle groups.
Close grip bench press variations
Looking to add some excitement and variety to your training routine? Incorporating different variations of the close grip bench press can help you break through plateaus and build strength in new ways. Whether you’re a seasoned lifter or just starting out, these variations offer a fresh take on the classic exercise, targeting your triceps, shoulders, and chest.
1. Dumbbell Close Grip Bench Press
Switching out the barbell for dumbbells can provide a different challenge to your muscles and improve stability. By using dumbbells, you’ll also engage more stabilizer muscles, enhancing your overall upper body strength. Start with lighter weights and gradually increase as you become comfortable with the movement.
2. Tempo Close Grip Bench Press
Adding a tempo to your close grip bench press can intensify the exercise and help you build control and endurance. By slowing down the eccentric (lowering) and concentric (lifting) phases of the movement, you’ll increase time under tension, promoting muscle growth and strength development.
3. Pause Reps
This variation involves incorporating pauses at different points during the exercise. For example, you can pause at the bottom position, an inch off the chest, or halfway through the movement. Pausing forces your muscles to work harder to initiate the lift, leading to increased muscle activation and strength gains.
Pro Tip: Incorporate close grip bench press variations into your training routine every 4-6 weeks to keep your muscles challenged and prevent stagnation.
Remember to choose a weight that allows you to maintain proper form throughout the exercise. Focus on quality repetitions rather than quantity. Gradually increase the weight as your strength improves.
Explore these variations and experiment with different combinations to find what works best for you. Remember to always warm up properly and consult with a fitness professional or coach if you have any concerns or questions about form or technique.
Close grip bench press vs. traditional bench press
When it comes to upper body strength training, two popular exercises often come to mind: the close grip bench press and the traditional bench press. While both exercises target the chest, shoulders, and triceps, they differ in their execution and focus. Understanding the differences between these two exercises can help you determine which one is best suited for your fitness goals and training needs.
The close grip bench press is performed by grasping the barbell with a narrower grip than the traditional bench press. This narrower grip places more emphasis on the triceps and shoulders, making it an ideal exercise for individuals looking to build tricep strength and improve pressing power. The close grip bench press also allows for a greater range of motion, targeting the triceps more effectively.
On the other hand, the traditional bench press is performed with a wider grip, engaging the pectoral muscles to a greater extent. This exercise is known for its ability to develop chest strength and size. The wider grip also activates the front deltoids, contributing to overall shoulder development. The traditional bench press is often favored by powerlifters and individuals aiming to increase their overall pressing strength.
While both exercises have their own unique benefits, they can be incorporated into your training routine based on your specific goals. If your primary focus is tricep development and pressing power, the close grip bench press is an excellent choice. Conversely, if you are looking to build a bigger chest and overall upper body strength, the traditional bench press is a staple exercise.
To help you better understand the differences between the close grip bench press and the traditional bench press, take a look at the following table:
| Exercise | Main Muscle Targeted | Secondary Muscles Engaged | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Close Grip Bench Press | Triceps | Shoulders | Improved tricep development and pressing power |
| Traditional Bench Press | Chest | Shoulders, Triceps | Overall chest and upper body strength development |
By comparing the close grip bench press and the traditional bench press, you can determine which exercise aligns best with your goals and preferences. Whether you choose the close grip bench press or the traditional bench press, make sure to prioritize proper form and gradually increase the weight as you progress. Combine these exercises with other complementary movements to create a well-rounded upper body training program.
Incorporating close grip bench press into your workout routine
Are you ready to take your upper body strength gains to the next level? Incorporating the close grip bench press into your training routine is a powerful way to do just that. But why stop there? By combining this exercise with other movements like power cleans, you can unlock even greater results. Let’s dive into the details of how to effectively incorporate the close grip bench press and power cleans into your workout routine.
The Close Grip Bench Press and Its Benefits
The close grip bench press is a variation of the traditional bench press that places more emphasis on the triceps, requiring a narrower hand position on the barbell. By reducing the width of your grip, you activate the triceps to a greater extent, leading to enhanced tricep development and improved pushing power. Additionally, the close grip bench press also engages the chest and shoulders, providing a comprehensive upper body workout.
The close grip bench press is a versatile exercise that targets multiple muscle groups in the upper body. When combined with power cleans, it can create a potent training stimulus for overall strength and performance gains.
Maximizing Upper Body Strength Gains
Incorporating the close grip bench press and power cleans into your routine requires a strategic approach. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you make the most out of these exercises:
- Step 1: Establish a Solid Foundation
Prioritize proper form and technique for both the close grip bench press and power cleans. Begin with lighter weights to focus on building a solid foundation and mastering the movements. - Step 2: Alternate Between Exercises
Integrate close grip bench press and power cleans into your workouts on separate days. This allows for adequate recovery and prevents overexertion of specific muscle groups. - Step 3: Vary Reps and Sets
Mix up your training program by alternating between different rep ranges and set combinations. This variation challenges your muscles and prevents plateauing. - Step 4: Engage the Hips
While the close grip bench press mainly targets the upper body, you can enhance overall performance by engaging your hips during the exercise. Focus on maintaining a stable and strong core.
Sample Workout Routine
To help you get started, here’s a sample workout routine that incorporates close grip bench press and power cleans:
| Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 |
|---|---|---|
| Close Grip Bench Press (5 sets x 8 reps) | Rest Day | Power Cleans (4 sets x 6 reps) |
| Shoulder Press (3 sets x 10 reps) | Rest Day | Incline Dumbbell Press (4 sets x 8 reps) |
| Tricep Pushdowns (3 sets x 12 reps) | Rest Day | Barbell Rows (3 sets x 10 reps) |

Remember to adjust the weights and repetitions based on your individual fitness level and goals. It’s essential to listen to your body and gradually progress over time.
By incorporating the close grip bench press and power cleans into your workout routine, you can create an effective synergy that enhances your upper body strength, tricep development, and overall performance. Follow the steps outlined here, stay consistent, and enjoy the results that this powerful combination can offer.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering the close grip bench press is essential for enhancing upper body strength and tricep development. By following the proper technique and incorporating variations into your training routine, you can achieve your fitness goals more effectively.
The close grip bench press specifically targets the triceps, chest, and shoulders, making it a valuable exercise for athletes and fitness enthusiasts alike. By focusing on proper form and technique, you can maximize the benefits of this exercise and see significant improvements in your upper body strength.
Furthermore, incorporating variations of the close grip bench press adds variety to your training routine and challenges your muscles in different ways. Whether you choose to use dumbbells, incorporate tempo and pause reps, or combine it with other exercises, such as power cleans, you can continue progressing and pushing your limits.
By making the close grip bench press a staple in your workout routine, you will not only enhance your upper body strength and tricep development but also improve other pushing movements. So start implementing the close grip bench press today and take your training to new heights!
FAQ
How is the close grip bench press different from the traditional bench press?
The close grip bench press differs from the traditional bench press in hand placement and muscle emphasis. With the close grip bench press, your hands are positioned closer together, placing more focus on the triceps. In contrast, the traditional bench press utilizes a wider grip, targeting the chest and shoulders more prominently.
What are the benefits of incorporating close grip bench press into my workout routine?
By including close grip bench press in your training regimen, you can experience several benefits. This exercise is excellent for strengthening and developing the triceps, improving upper body pushing power, and enhancing overall upper body strength. Additionally, it can help increase muscle definition and contribute to better athletic performance.
How can I enhance my tricep development with close grip bench press?
Close grip bench press is an effective exercise for targeting and developing the triceps. To enhance tricep development further, focus on proper form and technique, gradually increase the weight used, and incorporate different variations of the exercise. By consistently challenging your triceps and providing progressive overload, you can maximize muscle growth and strength gains.
What are some variations of the close grip bench press?
There are several variations of the close grip bench press that you can incorporate into your training routine. Some options include using dumbbells instead of a barbell, performing tempo reps by controlling the lowering and lifting phases of the exercise, and incorporating pause reps where you briefly pause at the bottom position. These variations can add variety to your workouts and help stimulate muscle growth and strength gains.
How can I incorporate close grip bench press into my workout routine?
To effectively incorporate close grip bench press into your training routine, consider including it as a primary upper body compound movement. You can perform close grip bench press alongside other exercises such as power cleans to target different muscle groups and enhance overall strength gains. Remember to prioritize proper form, gradually increase the weight you lift, and allow adequate rest and recovery between sessions for optimal results.
What You Need to Know About deadlift muscles worked
Are you looking to take your strength and fitness to the next level? Look no further than the deadlift, a fundamental pull exercise that engages multiple muscle groups for maximum results. But have you ever wondered which muscles are truly worked during this powerful movement? Let’s dive deep and uncover the secrets behind deadlift muscles worked and how they can transform your fitness journey.
Key Takeaways:
- The deadlift is a compound exercise that targets the muscles in the posterior chain, including the back, glutes, and hamstrings.
- Primary muscles engaged during the deadlift include the erector spinae, gluteus maximus, hamstrings, and quadriceps.
- In addition to the lower body, the grip muscles and upper body also contribute to stabilizing the movement.
- Incorporating deadlifts into your routine can lead to increased strength, improved posture, and enhanced overall functional fitness.
- Proper form and technique are crucial for maximizing the benefits and minimizing the risk of injury during deadlifts.
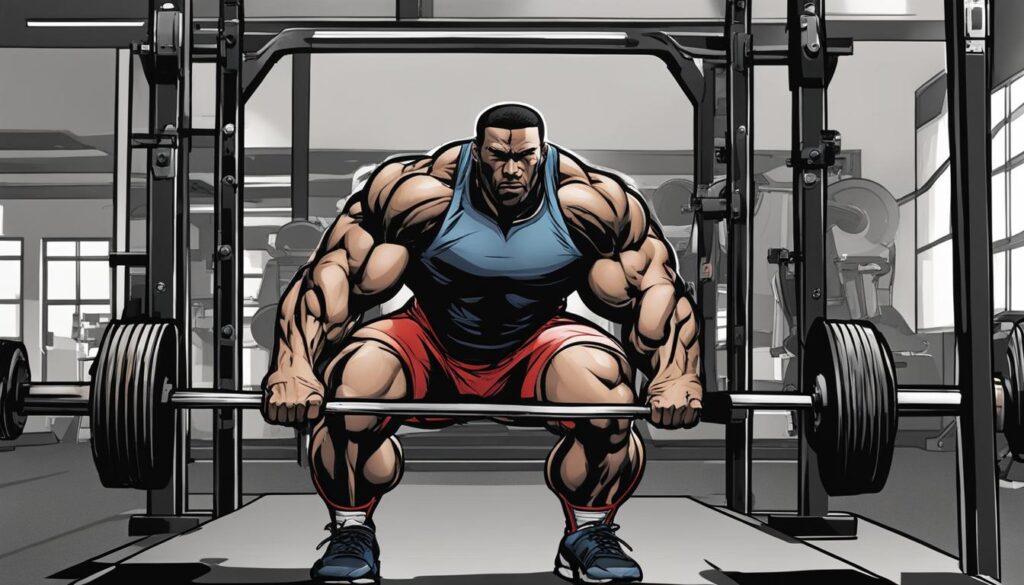
Understanding the Deadlift Exercise
Before we delve into the specific muscles worked during the deadlift, let’s first understand the mechanics of this exercise. The deadlift is a compound movement that primarily targets the muscles in the posterior chain, including the back, glutes, and hamstrings. It is a pulling exercise that involves gripping the barbell and lifting it from the ground to a standing position.
The deadlift is considered one of the most effective pull exercises for developing overall strength and muscle mass. It engages multiple muscle groups in the body, making it a highly efficient workout.
Deadlift Mechanics
To perform a deadlift, start by standing with your feet shoulder-width apart and the barbell on the ground in front of you. Keep your back straight and core engaged. Bend your knees and hinge at the hips, maintaining a neutral spine position.
As you grip the barbell, make sure your hands are slightly wider than shoulder-width apart. Your palms can face down (overhand grip), or one palm can face up and the other down (mixed grip). Having a solid grip on the bar is essential for a successful deadlift.
When you’re ready, push through your heels and lift the barbell by extending your hips and straightening your legs. As you lift, engage your back, glutes, and hamstrings to drive the movement. Keep the barbell close to your body throughout the exercise to maintain proper form and reduce the risk of injury.
“The deadlift is a foundational exercise that targets multiple muscle groups, making it an excellent choice for overall strength and muscle development.” – Fitness Expert
At the top of the movement, stand tall with your shoulders pulled back and the barbell in full extension. Slowly lower the barbell back down to the ground in a controlled manner, maintaining proper form and body alignment.
It’s important to note that the deadlift can be modified to suit individual fitness levels and goals. Variations, such as the sumo deadlift and Romanian deadlift, target different muscle groups while still providing similar benefits.
Now that we have a better understanding of how the deadlift exercise works and its mechanics, let’s explore the specific muscles that are engaged during this compound movement in the next section.
Primary Muscles Engaged in the Deadlift
The deadlift is a compound exercise that activates multiple muscle groups, making it an excellent choice for full-body strength and development. Let’s take a closer look at the primary muscles worked during the deadlift.
The Posterior Chain
The deadlift primarily targets the muscles in the posterior chain. These muscles are located on the back side of the body and include the erector spinae in the lower back, the gluteus maximus in the buttocks, and the hamstrings at the back of the thighs.
The erector spinae muscles play a crucial role in maintaining a neutral spine during the deadlift, providing stability and preventing injury. The gluteus maximus is the largest muscle in the body and is responsible for hip extension, which is essential for lifting the weight off the ground. The hamstrings work in conjunction with the glutes to control the movement and assist in hip extension.
The Quadriceps
Although the deadlift primarily targets the posterior chain, it also engages the quadriceps at the front of the thighs. These muscles help to extend the knees and play a supporting role in the lifting process.
The grip muscles and the upper body also come into play during the deadlift, working to stabilize the movement and maintain control throughout the exercise.
To visualize the primary muscles engaged during the deadlift, refer to the table below:
| Muscle Group | Primary Muscles |
|---|---|
| Posterior Chain | Erector Spinae, Gluteus Maximus, Hamstrings |
| Quadriceps | Rectus Femoris, Vastus Lateralis, Vastus Medialis, Vastus Intermedius |
| Grip and Upper Body | Forearm Flexors, Latissimus Dorsi, Trapezius, Rhomboids |

The deadlift is a highly effective exercise for building overall strength, enhancing muscle development, and improving functional fitness. By engaging the primary muscles mentioned above, the deadlift provides a full-body challenge and promotes strength gains in key areas.
A proper deadlift targets the posterior chain, quadriceps, and upper body muscles, making it a comprehensive exercise for building strength and stability.
Benefits of Deadlift for Overall Strength and Fitness
Incorporating deadlifts into your workout routine can have numerous benefits for your overall strength and fitness. This compound exercise targets major muscle groups, promoting strength gains in the back, glutes, hamstrings, and quads. Additionally, deadlifts help improve posture, increase grip strength, boost athletic performance, and enhance overall functional fitness.
Deadlifts are a highly effective exercise for developing strength and power. By engaging multiple muscle groups simultaneously, such as the back, glutes, hamstrings, and quads, deadlifts can lead to substantial gains in overall strength and fitness. The deadlift is a compound movement that activates both the lower and upper body, making it a highly efficient exercise for maximizing caloric expenditure and promoting muscle growth.
One of the key benefits of deadlifts is their ability to improve posture. The exercise targets the muscles responsible for keeping the spine stable and erect, such as the erector spinae. Regular deadlift training can help strengthen these muscles, leading to better posture and decreased risk of back pain or injury.
Another advantage of deadlifts is their ability to increase grip strength. Holding onto a loaded barbell during a deadlift requires a significant amount of grip strength and forearm activation. By regularly performing deadlifts, you can develop a strong grip that can carry over to other exercises and activities, such as lifting weights or participating in sports.
Deadlifts are also valuable for improving athletic performance. The movement pattern and muscle activation involved in deadlifting closely mimic many real-life activities and sports movements. By strengthening the muscles involved in these movements, deadlifts can enhance explosive power, speed, and agility, leading to improved athletic performance in various sports.
Furthermore, deadlifts contribute to overall functional fitness, which refers to the ability to perform daily activities and tasks with ease and efficiency. By targeting multiple muscle groups and movements in a coordinated manner, deadlifts train the body to move and function as a unit. This can improve performance in everyday activities, such as lifting heavy objects, climbing stairs, or bending down to pick up items.
In summary, incorporating deadlifts into your workout routine can provide a plethora of benefits for your overall strength and fitness. This compound exercise targets major muscle groups, improves posture, increases grip strength, boosts athletic performance, and enhances overall functional fitness. However, it’s important to consult with a fitness professional to ensure proper form and technique when performing deadlifts to minimize the risk of injury and maximize the benefits.
Performing Deadlifts Properly
To maximize the benefits of deadlifts and minimize the risk of injury, it is crucial to perform the exercise with proper form. Here are some key tips to ensure you get the most out of your deadlift workout at the gym:
- Start with the right weight: Choose a weight that you can comfortably lift while maintaining proper form.
- Maintain a neutral spine: Focus on keeping your spine in a neutral position throughout the movement. Avoid rounding or arching your back.
- Engage your core: Activate your core muscles to provide stability and support during the exercise.
- Hinge at the hips: Initiate the movement by hinging at the hips, pushing your buttocks back while keeping your chest lifted.
- Drive through your heels: As you lift the barbell, push through your heels to generate power and maintain stability.
Proper technique is essential for optimizing the benefits of deadlifts and preventing injury. If you’re new to deadlifting or are unsure about your form, consider working with a knowledgeable fitness professional who can guide you through the correct technique.
Conclusion
The deadlift is a highly effective compound exercise that targets multiple muscles in the posterior chain, including the back, glutes, and hamstrings. By incorporating deadlifts into your regular workout routine, you can significantly enhance your overall strength and fitness levels. This fundamental pull exercise engages major muscle groups, promoting strength gains and increasing muscular endurance.
When performing deadlifts, it is crucial to prioritize proper form and technique to ensure both safety and optimal results. Start with a weight that allows you to maintain proper form throughout the movement, and focus on maintaining a neutral spine and engaging your core. Remember to hinge at the hips, drive through your heels, and stand tall, utilizing the power of your legs, glutes, and back.
Not only does the deadlift improve muscle strength and power, but it also has numerous benefits for your overall fitness. This exercise helps improve posture, increase grip strength, and enhance functional fitness, making your day-to-day activities easier and more efficient. Deadlifts are a versatile exercise that can be modified to suit various fitness levels and goals, making them a valuable addition to any workout routine.
In conclusion, the deadlift is a cornerstone exercise for building strength, improving fitness, and targeting the muscles of the posterior chain. Incorporate deadlifts into your training regimen, under proper guidance, to achieve impressive strength gains and take your fitness journey to new heights. Remember to prioritize proper form, stay consistent, and enjoy the transformative benefits this exercise has to offer!
FAQ
What muscles are worked during a deadlift?
The deadlift primarily engages the muscles in the posterior chain, including the erector spinae in the lower back, the gluteus maximus in the buttocks, the hamstrings at the back of the thighs, and the quadriceps at the front of the thighs. The grip muscles and the upper body also contribute to stabilizing the movement.
How does the deadlift exercise benefit overall strength and fitness?
Incorporating deadlifts into your workout routine can lead to significant strength gains in the back, glutes, hamstrings, and quads. Deadlifts also improve posture, increase grip strength, enhance athletic performance, and promote overall functional fitness.
What is the proper form for performing deadlifts?
To perform deadlifts properly, start with a weight that you can comfortably lift. Maintain a neutral spine throughout the movement by engaging your core. Hinge at the hips and drive through your heels to stand tall. It is advisable to work with a knowledgeable fitness professional to learn and practice the correct technique.
Why You Should Try hip thrust
Did you know that the glute muscles, specifically the gluteus maximus, are the largest muscle group in the human body? However, many people neglect to give these powerhouse muscles the attention they deserve in their fitness routines.
If you’re looking to take your workouts to the next level and achieve a stronger posterior chain, incorporating hip thrusts into your fitness routine is the way to go. This often overlooked exercise has been gaining popularity for its ability to strengthen the glutes, improve athletic performance, and enhance overall body aesthetics.
Key Takeaways:
- Hip thrusts target and strengthen the glute muscles, the largest muscle group in the body.
- Incorporating hip thrusts into your fitness routine can lead to firmer and more sculpted glutes.
- Hip thrusts can improve athletic performance by increasing power and force production.
- Proper form and technique are crucial for maximizing the benefits of hip thrusts and preventing injuries.
- There are various hip thrust variations and complementary exercises that can intensify your glute training.
Strengthening Your Glutes with Hip Thrusts
When it comes to building strong, well-defined glutes, hip thrusts are a must-have exercise in your fitness routine. Not only do they target your glute muscles directly, but they also activate the surrounding muscles, resulting in a firmer and more sculpted behind.
The mechanics behind hip thrusts are simple yet effective. As you perform the exercise, you start in a seated position with your back against a bench, knees bent, and feet flat on the ground. With a loaded barbell positioned across your hips, you contract your glutes, driving your hips upward until your body is in a straight line from your knees to your shoulders.
By using your glutes to lift the weight, hip thrusts activate and strengthen the gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, and gluteus minimus muscles. These powerful muscles not only improve the aesthetics of your posterior, but they also play a crucial role in hip extension, stability, and overall lower body strength.
The Benefits of Glute Strengthening
Strengthening your glutes through hip thrusts can offer a range of benefits beyond a shapely behind. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Improved Athletic Performance: Strong glutes are essential for generating power and explosiveness in various athletic movements, such as running, jumping, and squatting.
- Injury Prevention: Weak glutes can contribute to imbalances in your lower body, leading to issues like knee pain, lower back pain, and hip instability. Strengthening your glutes with hip thrusts can help prevent these injuries.
- Enhanced Posture: Having strong glutes can improve your posture by aligning your pelvis and reducing the likelihood of lower back pain and postural imbalances.
- Increased Lower Body Strength: Strong glutes are crucial for performing compound exercises like squats and deadlifts. By incorporating hip thrusts into your routine, you’ll strengthen your glutes and improve your overall lower body strength.
So, if you’re looking to transform your glutes and boost your lower body strength, hip thrusts are an exercise you definitely want to incorporate into your fitness routine.
| Exercise | Description |
|---|---|
| Hip Thrust | This exercise involves sitting with your back against a bench, knees bent, feet flat on the ground, and a loaded barbell positioned across your hips. By contracting your glutes, you drive your hips upward until your body is in a straight line from your knees to your shoulders. |
| Glute Bridge | Similar to hip thrusts, the glute bridge involves lying on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the ground. By engaging your glutes, you lift your hips off the ground until your body forms a straight line from your knees to your shoulders. |
| Single-Leg Hip Thrust | This variation of the hip thrust is performed with one leg extended straight out. It engages your glutes asymmetrically and provides a greater challenge for stability and strength. |
Utilizing various hip thrust variations can target your glutes from different angles and intensities, allowing for a well-rounded glute training program.
Improving Athletic Performance with Hip Thrusts
When it comes to enhancing athletic performance, hip thrusts are a game-changer. Whether you’re an aspiring athlete, a seasoned runner, or a weightlifting enthusiast, incorporating hip thrusts into your training regimen can take your performance to the next level. This powerful exercise targets your glutes, helps generate more power, and improves force production, all of which are crucial for excelling in your chosen sport.
By engaging the muscles in your glutes, hip thrusts strengthen the posterior chain, which includes the muscles along your backside, from your glutes to your hamstrings. A strong posterior chain is vital for various athletic movements, such as sprinting, jumping, and lifting. When you perform hip thrusts correctly and consistently, you not only develop stronger glutes but also improve your overall athleticism and explosiveness.
| Benefits | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased Power | Generating more power in explosive movements like sprinting and jumping. |
| Improved Force Production | Better ability to exert force against resistance, enhancing strength and performance. |
| Enhanced Speed and Agility | Developing stronger glutes and hamstrings for faster movements and quick direction changes. |
| Reduced Risk of Injury | Strengthening the muscles that support and stabilize your lower body, minimizing the risk of common sports injuries. |
It’s important to note that proper form and technique are key to reaping the full benefits of hip thrusts. When executing the exercise, focus on driving through your heels, engaging your glutes, and maintaining a neutral spine. Gradually increase the intensity by adding weights or resistance bands as your strength improves.
Start incorporating hip thrusts into your training routine and unleash your athletic potential. Whether you’re striving for a new personal record or simply aiming to perform at your best, hip thrusts can make a significant impact on your athletic performance.
Hip Thrusts in Your Fitness Routine
Integrating hip thrusts into your fitness routine can be a game-changer. These exercises specifically target your glute muscles, helping you achieve a firmer and more sculpted behind. Whether you prefer working out at the gym or in the comfort of your own home, I will provide you with tips and guidance on how to effectively incorporate hip thrusts into your existing exercise plan.
To begin, it’s important to understand the proper form and technique for hip thrusts. Start by positioning yourself on the edge of a bench or a sturdy surface with your upper back resting against it. Bend your knees and plant your feet firmly on the ground, slightly wider than hip-width apart.
Tips for Proper Hip Thrust Form:
- Engage your core as you lift your hips off the ground, pressing through your heels.
- Squeeze your glutes at the top of the movement to maximize the contraction.
- Lower your hips back down slowly, maintaining control throughout the motion.
As you become more comfortable with the exercise, you can gradually increase the intensity by adding weights such as barbells, dumbbells, or resistance bands. These additional resistance tools can provide extra challenge and help you progress in your hip thrust journey.
Furthermore, you can incorporate variations of hip thrusts to target different areas of your glutes and add variety to your routine. Experiment with different foot positions, such as a wider stance or a narrower stance, to place emphasis on specific muscle groups.
Sample Hip Thrust Variations:
- Single-Leg Hip Thrusts: Perform the exercise with only one leg planted on the ground, while the other leg is extended straight in front of you. This variation intensifies the focus on each individual glute.
- Elevated Hip Thrusts: Place your feet on an elevated surface, such as a step or a stability ball, to increase the range of motion and engage your glutes at a deeper level.
- Resistance Band Hip Thrusts: Wrap a resistance band around your thighs, just above your knees, to add resistance and activate your hip abductors for additional glute activation.
Remember, consistency is key when incorporating hip thrusts into your fitness routine. Aim to perform the exercise at least twice a week, gradually increasing the number of sets and reps as you progress.
Quote: “Hip thrusts are a powerful exercise that can transform your glutes and overall physique. By incorporating them into your fitness routine, you’ll be on your way to building stronger and more defined glutes.” – Fitness Expert
With proper form and technique, along with consistent dedication, you’ll soon reap the benefits of hip thrusts in your fitness journey. Stronger glutes not only enhance your physical appearance but also improve your overall athletic performance and daily activities. So why wait? Start incorporating hip thrusts into your fitness routine today and experience the incredible results for yourself.
Maximizing Hip Thrusts with Variations
Incorporating variations into your hip thrust workouts can take your glute training to the next level. By introducing different techniques and equipment, you can target your glutes from multiple angles and intensify the effectiveness of your hip thrusts.
Here are some variations to consider:
- Weighted Hip Thrusts: Add a barbell or dumbbells to increase resistance, challenging your glutes with added weight.
- Resistance Band Hip Thrusts: Loop a resistance band above your knees or around your hips to activate the glute muscles even more during the movement.
- Single-Leg Hip Thrusts: Elevate one foot off the ground while performing the hip thrust, emphasizing one glute at a time and improving balance and stability.
- Wide Stance Hip Thrusts: Position your feet wider apart to engage the outer glute muscles and target the hip abductors.
- Narrow Stance Hip Thrusts: Bring your feet closer together to emphasize the inner glute muscles and increase the difficulty of the exercise.
- Elevated Hip Thrusts: Place your shoulders on a step or bench, allowing for a greater range of motion and deeper glute activation.
- Pause Rep Hip Thrusts: Hold the contracted position for a few seconds at the top of each repetition to intensify the muscle engagement.
Remember to gradually incorporate these variations into your routine and listen to your body. Start with lighter weights or lower resistance bands and gradually increase the difficulty as your strength and technique improve. Always prioritize proper form and range of motion to avoid injuries and get the most out of each variation.
Experimenting with these hip thrust variations will not only keep your workouts exciting and challenging but also ensure that you continue making progress in building stronger and more defined glutes. Now, let’s explore complementary exercises that can further enhance your glute strength when combined with hip thrusts.
Complementary Exercises to Boost Glute Strength
When it comes to building strong glutes, incorporating a variety of exercises into your routine is key. While hip thrusts are excellent for targeting and strengthening the glutes, combining them with complementary exercises can take your glute strength to the next level. Let’s take a look at two effective exercises: pull-ups and close grip movements.
Pull-Ups for Glute Activation
Pull-ups are a compound exercise that primarily target the muscles in your back, but did you know they can also activate your glutes? By initiating the movement from your glutes, you engage these muscles and make them work in conjunction with your back muscles.
To perform pull-ups, start by gripping the bar with your palms facing away from you, hands slightly wider than shoulder-width apart. Hang from the bar with your arms fully extended. Begin the movement by squeezing your glutes and pulling your shoulder blades down and back. As you lift your body up towards the bar, focus on contracting your glutes to help drive the movement. Lower yourself back down with control and repeat for the desired number of reps.
Close Grip Movements for Glute Strength
Close grip exercises, such as close grip bench presses or rows, are another excellent way to complement your hip thrusts and further develop glute strength. These exercises target the muscles in your upper body, particularly the triceps and back muscles, and engage the glutes as stabilizers.
Incorporate close grip bench presses into your workout by lying on a bench with your hands placed shoulder-width apart on the barbell. Lower the barbell towards your chest, keeping your elbows close to your body. Push the barbell back up to the starting position, focusing on engaging your glutes throughout the movement.
For close grip rows, stand with your feet hip-width apart, holding a barbell with an overhand grip, hands shoulder-width apart. Lean forward slightly, maintaining a neutral spine. Pull the barbell towards your lower chest, squeezing your shoulder blades together and engaging your glutes. Lower the barbell back down and repeat.
Combining Exercises for Stronger Glutes
By incorporating pull-ups and close grip movements into your glute training routine, you target multiple muscle groups that support and work synergistically with your glutes. This comprehensive approach ensures that your glutes are not the only muscles being strengthened but also those that contribute to overall stability and strength.
Remember, it’s important to prioritize proper form and technique to maximize the effectiveness of these exercises. Start with lighter weights or modifications, gradually increasing the challenge as you become more comfortable and confident with the movements.
Unlock the full potential of your glutes by integrating pull-ups and close grip exercises into your workout routine. Combine these exercises with hip thrusts for a well-rounded glute training regimen that will help you achieve your strength and fitness goals.
In the next section, we’ll explore the importance of maintaining proper form and technique while performing hip thrusts for optimal results.
The Importance of Proper Form and Technique
When it comes to performing hip thrusts, maintaining proper form and technique is crucial for maximizing the effectiveness of this exercise and minimizing the risk of injury. Here are some important tips and cues to keep in mind:
- Align your body: Begin by positioning your upper back against a stable surface, such as a bench or step. Your feet should be flat on the ground, shoulder-width apart, and knees bent at a 90-degree angle. This alignment ensures stability throughout the movement.
- Engage your core: Before initiating the hip thrust, engage your core muscles by drawing your navel towards your spine. This will provide stability to your spine and prevent any excessive arching or overarching during the exercise.
- Maintain a neutral spine: Throughout the entire movement, focus on maintaining a neutral spine position by avoiding excessive curvature (hyperextension) or rounding (flexion) of the lower back. This helps target the glute muscles effectively and protects your spine from unnecessary stress.
- Squeeze your glutes: As you lift your hips off the ground, make sure to squeeze your glute muscles forcefully at the top of the movement. This contraction will maximize the activation of the glutes and contribute to their strength development.
- Control the descent: Lower your hips back down to the starting position in a controlled manner. Avoid allowing your hips to drop too quickly or collapsing your lower back. Maintain tension in your glutes throughout the entire range of motion.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure that you are performing hip thrusts with proper form and technique, allowing you to reap the full benefits of this exercise and achieve optimal results.
Benefits of Proper Form and Technique
Executing hip thrusts with proper form and technique not only minimizes the risk of injury but also maximizes the recruitment of the glute muscles. When performed incorrectly, hip thrusts may place excessive stress on the lower back or fail to effectively target the glutes.
By employing the correct form and technique, you’ll experience the following benefits:
| Benefits of Proper Form and Technique for Hip Thrusts |
|---|
| 1. Reduced risk of lower back strain or injury due to spinal alignment |
| 2. Increased activation and engagement of the glute muscles |
| 3. Improved glute strength and development |
| 4. Enhanced stability and balance during the exercise |
Overcoming Common Challenges with Hip Thrusts
Performing hip thrusts can present some challenges that may hinder your progress. However, with the right guidance and modifications, you can overcome these obstacles and continue your journey toward stronger glutes and improved athletic performance. In this section, I will address the common challenges faced by individuals when performing hip thrusts and provide practical solutions to help you overcome them.
1. Struggling with Balance
One common challenge many people face when performing hip thrusts is maintaining balance throughout the exercise. This can be particularly challenging, especially for beginners. To improve your balance, try the following tips:
- Place your feet shoulder-width apart and firmly on the ground.
- Engage your core muscles to stabilize your body.
- Start with bodyweight hip thrusts and gradually increase the difficulty by adding weights.
- Try using a stability ball or bench for support.
2. Experiencing Discomfort or Pain
Another challenge that some individuals encounter is discomfort or pain while performing hip thrusts. This can occur due to incorrect form or muscle imbalances. To alleviate discomfort and ensure proper execution, consider the following solutions:
- Focus on proper alignment by keeping your hips, knees, and ankles in line throughout the exercise.
- Gradually increase the intensity and range of motion to allow your muscles to adapt over time.
- Perform exercises that target hip flexors and hamstrings to maintain balanced muscle development.
- Consult with a fitness professional or physical therapist if the discomfort persists or worsens.
3. Plateauing in Strength and Progress
At times, you may find that your strength and progress in hip thrusts reach a plateau. This can be frustrating, but there are strategies you can implement to overcome this challenge:
- Incorporate variations of hip thrusts, such as single-leg hip thrusts or banded hip thrusts, to target your glutes from different angles.
- Change up your workout routine by incorporating other glute-strengthening exercises and focusing on progressive overload.
- Ensure you are fueling your body with a balanced diet that supports muscle recovery and growth.
- Listen to your body and give yourself adequate rest and recovery time to prevent overtraining.
By implementing these strategies and modifications, you can overcome the challenges associated with hip thrusts and continue to make progress toward achieving your fitness goals. Remember, consistency and patience are key in any fitness journey.
Conclusion
Throughout this article, we have explored the numerous benefits of incorporating hip thrusts into your fitness routine. Not only do hip thrusts strengthen your glutes, but they also have a positive impact on your overall athletic performance. By engaging the glute muscles, hip thrusts help you achieve a firmer and more sculpted behind, enhancing your physique and boosting your confidence.
We have also emphasized the importance of proper form and technique while performing hip thrusts. By maintaining correct alignment and executing the exercise with precision, you can maximize the effectiveness of each repetition and minimize the risk of injury. Remember to start with lighter weights and gradually increase the load as your strength improves, ensuring a progressive and safe training experience.
Now that you understand the benefits and proper technique, it’s time to put this knowledge into action. Start implementing hip thrusts into your workout routine and experience the incredible improvements they can bring to your posterior chain and overall athletic performance. Whether you’re a seasoned athlete or just beginning your fitness journey, hip thrusts offer a versatile and effective exercise to help you reach your goals.
FAQ
What are the benefits of incorporating hip thrusts into my fitness routine?
Incorporating hip thrusts into your fitness routine can have numerous benefits. They strengthen your glutes, improve athletic performance, and enhance your overall workouts.
How do hip thrusts target and strengthen my glute muscles?
Hip thrusts specifically target and strengthen your glute muscles. By performing this exercise, you activate and engage your glutes, leading to firmer and more sculpted behind.
How can hip thrusts improve my athletic performance?
Hip thrusts can enhance your athletic performance by increasing power and force production. Whether you’re a runner or a weightlifter, incorporating hip thrusts into your training regimen can improve your overall athletic performance.
How can I incorporate hip thrusts into my fitness routine?
You can effectively incorporate hip thrusts into your fitness routine by following proper form and technique. Whether you’re at the gym or at home, there are tips and guidance available to help you seamlessly integrate hip thrusts into your existing exercise plan.
Can I vary my hip thrusts to maximize their effectiveness?
Yes, you can maximize the effectiveness of hip thrusts by incorporating variations into your workouts. These variations include using weights or resistance bands and experimenting with different foot positions and ranges of motion.
Are there any complementary exercises that can boost glute strength alongside hip thrusts?
Yes, there are complementary exercises that can further enhance glute strength when combined with hip thrusts. Exercises like pull-ups and close grip exercises engage other muscle groups that support and work synergistically with your glutes, ensuring a well-rounded glute training routine.
What is the importance of maintaining proper form and technique when performing hip thrusts?
It is crucial to maintain proper form and technique while performing hip thrusts. This ensures that you execute the exercise correctly, minimizing the risk of injury, and maximizing the effectiveness of each repetition.
What are some common challenges individuals face with hip thrusts, and how can they be overcome?
Common challenges individuals often face with hip thrusts include struggling with balance and experiencing discomfort. These challenges can be overcome through modifications and solutions such as adjusting foot placement, utilizing stability equipment, or seeking professional guidance.
Can you provide a summary of the key points discussed about hip thrusts?
Hip thrusts offer several benefits when incorporated into your fitness routine, including strengthening your glutes, improving athletic performance, and optimizing your workouts. It is essential to perform them with proper form and technique and to overcome common challenges by making adjustments or seeking professional guidance.
Mastering kettlebell swings
Did you know that kettlebell swings can help you burn up to 20 calories per minute? That’s more than double the calorie burn of traditional cardiovascular exercises like running or cycling. If you’re looking to supercharge your workouts and achieve impressive results, incorporating kettlebell swings into your fitness routine is a game-changer. In this article, I will guide you through everything you need to know about mastering kettlebell swings, from the benefits they offer to the proper technique and advanced variations. Get ready to transform your workouts and take your fitness to new heights!
Key Takeaways:
- Kettlebell swings can help you burn up to 20 calories per minute, making them an efficient and effective exercise for weight loss.
- Incorporating kettlebell swings into your workouts can improve strength, cardiovascular endurance, core stability, and overall fitness levels.
- Proper technique is crucial for maximizing the benefits of kettlebell swings and preventing injuries. Focus on maintaining a neutral spine and engaging the hips and glutes.
- Gradually increase the weight of your kettlebell as you become more proficient to continue challenging your muscles and progressing in your fitness journey.
- Combine kettlebell swings with other exercises to create dynamic and well-rounded workout routines that target multiple muscle groups.
Understanding the Benefits
When it comes to getting the most out of your workouts, incorporating kettlebell swings into your routine can provide a range of benefits. This dynamic exercise engages multiple muscle groups while simultaneously increasing cardiovascular endurance, making it a highly efficient choice for improving overall fitness. Let’s take a closer look at some of the key advantages of kettlebell swings:
Building Strength
Kettlebell swings are a powerhouse exercise that targets the muscles in your glutes, hamstrings, and core. By swinging the kettlebell through your legs and explosively extending your hips, you activate these muscle groups and build functional strength that translates into better performance in everyday activities and sports.
Improving Cardiovascular Endurance
Not only do kettlebell swings help you build strength, but they also provide a great cardiovascular workout. The explosive, full-body movement involved in swinging the kettlebell raises your heart rate, improving your cardiovascular endurance over time. By incorporating kettlebell swings into your routine, you can enhance your stamina and boost your overall fitness level.
Enhancing Core Stability
Kettlebell swings require the engagement of your core muscles to maintain stability and control throughout the movement. As you swing the kettlebell, your core muscles work to stabilize your spine and pelvis, promoting better posture and reducing the risk of injury. By regularly performing kettlebell swings, you can develop a strong and stable core that supports your overall strength and balance.
Burning Calories
Kettlebell swings are a highly effective exercise for burning calories and promoting weight loss. The explosive nature of the movement demands significant energy expenditure, allowing you to torch calories and lose body fat. Additionally, the high-intensity nature of kettlebell swings keeps your heart rate elevated, maximizing the calorie burn during and after your workout.
Take a look at the table below for a summary of the benefits of kettlebell swings:
| Benefits of Kettlebell Swings |
|---|
| Builds strength in glutes, hamstrings, and core |
| Improves cardiovascular endurance |
| Enhances core stability |
| Burns calories and promotes weight loss |
As you can see, incorporating kettlebell swings into your workout routine can deliver a wide range of benefits. Not only will you build strength and endurance, but you’ll also enhance core stability and burn calories. So, if you’re looking to take your fitness to the next level, it’s time to grab a kettlebell and start swinging!
Proper Technique
When it comes to mastering kettlebell swings, proper technique is crucial for both safety and effectiveness. In this section, I will walk you through the correct technique for executing kettlebell swings. By following these guidelines, you can ensure proper integration of this exercise into your workout routine.
Stance and Grip
First, let’s talk about your stance. Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and toes slightly turned out. Maintain a slight bend in your knees and engage your core muscles.
Next, the grip. Grab the kettlebell handle with both hands, keeping your palms facing down. Make sure your thumbs are hooked around the handle for a secure grip.
To safely initiate the kettlebell swing, slightly hinge at the hips while maintaining a neutral spine. This means keeping your back straight and avoiding excessive rounding or arching.
Movement Pattern
Now that you’re in the proper starting position, let’s move onto the movement pattern of the kettlebell swing. The key to a successful swing is generating power from your hips and glutes.
Begin by swinging the kettlebell back between your legs, keeping your arms extended and maintaining control of the weight. As you initiate the upward swing, explosively thrust your hips forward, using the power of your lower body to propel the kettlebell forward and upward.
At the top of the swing, the kettlebell should be at chest height, with your arms extended and the weight in line with your body. Avoid overextending your back or lifting the weight with your shoulders. The force of the swing should come primarily from the hinge at your hips.
As the kettlebell descends, smoothly transition into the next repetition by allowing the weight to swing back between your legs, maintaining a fluid and controlled motion.
Remember to breathe throughout the exercise, inhaling as the kettlebell descends and exhaling as you thrust your hips forward during the upward swing.
Proper form and safety are paramount to prevent injuries while performing kettlebell swings. It is essential to keep the movement controlled and within your range of motion. Avoid using excessive weights that may compromise your technique.
It’s important to note that if you’re new to kettlebell swings or unsure of your form, it’s advised to seek guidance from a qualified fitness professional to ensure proper integration and minimize the risk of injury.
Summary
To perform kettlebell swings with proper technique, follow these key points:
- Stand with feet shoulder-width apart and maintain a slight bend in the knees.
- Grasp the kettlebell handle with both hands, keeping your palms facing down.
- Hinge at the hips while maintaining a neutral spine.
- Initiate the swing by thrusting your hips forward and explosively driving the kettlebell upward with your lower body.
- Keep your arms extended and the weight in line with your body at the top of the swing.
- Allow the kettlebell to swing back between your legs with a controlled motion.
By following these guidelines, you can safely and effectively incorporate kettlebell swings into your workout routine.
Integrating Kettlebell Swings into Workouts
Once you have mastered the technique and understood the benefits of kettlebell swings, it’s time to integrate this dynamic exercise into your existing workout routine. By incorporating kettlebell swings, you can add variety, challenge different muscle groups, and enhance the effectiveness of your workouts.
Here are some ways to seamlessly integrate kettlebell swings into your exercise regimen:
1. Warm-up Sets
Start your workout with a few sets of kettlebell swings as part of your warm-up routine. This not only increases blood flow and elevates your heart rate, but it also prepares your muscles for the upcoming exercises.
2. Superset with Other Exercises
Supersetting kettlebell swings with other exercises can create a powerful and efficient workout. Pairing kettlebell swings with exercises such as squats, lunges, or push-ups allows you to work multiple muscle groups in succession, maximizing your time in the gym.
3. Circuit Training
Include kettlebell swings in a circuit training routine for a high-intensity workout that targets both strength and cardiovascular endurance. Design a circuit that incorporates various exercises along with kettlebell swings, performing each exercise for a set amount of time before moving on to the next.
4. Tabata Intervals
Tabata intervals are a popular form of high-intensity interval training (HIIT) that involve short bursts of intense exercise followed by brief rest periods. Incorporate kettlebell swings into a Tabata workout, performing them at maximum effort for 20 seconds and then resting for 10 seconds. Repeat this cycle for a total of four minutes, alternating between kettlebell swings and other exercises.
5. Standalone Workouts
Kettlebell swings can also be the focus of a standalone workout. Design a routine that includes different variations of kettlebell swings, such as one-arm swings, staggered stance swings, or double kettlebell swings, to challenge your muscles from different angles.
Pro tip: Remember to listen to your body and adjust the intensity and volume of your workouts based on your fitness level and goals. It’s always important to prioritize proper form and safety to avoid injury.
| Workout Structure Example | Sets | Reps |
|---|---|---|
| Kettlebell Swing Circuit | 3 | 12-15 |
| Superset: Kettlebell Swing + Goblet Squat | 4 | 8-10 |
| Tabata Intervals: Kettlebell Swing | *See description above* | – |
| Kettlebell Swing Finisher | 1 | 20-25 |
Remember, the key to successfully integrating kettlebell swings into your workouts is balance and progression. Start with a weight that challenges you but allows for proper form, and gradually increase the intensity and volume over time. With consistency and dedication, kettlebell swings can be a valuable addition to your fitness routine, helping you achieve your goals and improve your overall strength and conditioning.
Starting Out: Beginner Weight Selection
If you are new to kettlebell swings, it’s important to start with an appropriate weight to ensure proper form and prevent injuries. Choosing the right weight will allow you to gradually build strength and progress in your workouts over time. Here are some recommendations to help you select a beginner weight:
- Assess your current fitness level: Consider your overall strength, endurance, and previous experience with weightlifting exercises. If you are a beginner or have limited strength training experience, start with a lighter kettlebell.
- Consult with a fitness professional: If you’re unsure about the right weight for you, it can be helpful to seek guidance from a certified personal trainer or kettlebell instructor. They can assess your fitness level and provide personalized recommendations.
- Start with a manageable weight: It’s better to start with a weight that feels lighter and allows you to focus on your form and technique. A weight that feels challenging but still manageable is ideal for beginners.
- Consider your goals: Think about your fitness goals and the intensity level you want to achieve. If your goal is to build strength and endurance, you may need to start with a slightly heavier weight than if your goal is primarily cardiovascular fitness.
Remember, it’s always better to start with a weight that feels too light rather than too heavy. As you become more proficient in kettlebell swings and your strength improves, you can gradually increase the weight to continue challenging yourself.
Tip: It’s important to listen to your body and pay attention to any discomfort or pain while performing kettlebell swings. If you experience any pain or struggle to maintain proper form with a particular weight, consider reducing the weight or seeking guidance from a fitness professional.
By starting with an appropriate beginner weight, you will be able to learn the proper technique, focus on your form, and minimize the risk of injuries. As you gain experience and confidence, you can gradually progress to heavier weights and reap the full benefits of kettlebell swings.
Targeting Specific Muscle Groups
Kettlebell swings are a highly effective exercise that works multiple muscle groups simultaneously. In this section, I will discuss the specific muscle groups that are primarily targeted during kettlebell swings and provide insights on how to modify the exercise to emphasize certain areas.
Primary Muscle Groups
During kettlebell swings, the following key muscle groups are actively engaged:
- Glutes: The gluteal muscles, including the gluteus maximus, medius, and minimus, play a significant role in generating power and explosiveness during the swing movement.
- Hamstrings: The posterior thigh muscles, specifically the semitendinosus, semimembranosus, and biceps femoris, work synergistically with the glutes to extend the hips and propel the kettlebell forward.
- Core: The deep core muscles, such as the rectus abdominis, obliques, and transverse abdominis, are essential for stabilizing the spine and maintaining proper form throughout the swing motion.
- Shoulders: The deltoids, trapezius, and rotator cuff muscles are actively involved in controlling and guiding the kettlebell’s trajectory during the swing.
By targeting these muscle groups simultaneously, kettlebell swings offer a comprehensive full-body workout that can strengthen and tone multiple areas in a time-efficient manner.
Modifications for Muscle Emphasis
While kettlebell swings effectively engage multiple muscle groups, you can modify the exercise to place greater emphasis on certain areas. Here are a few variations:
- To target the glutes more intensely, try performing a glute bridge press at the top of each swing. As you thrust your hips forward, squeeze your glutes and lift your upper body off the floor, creating a bridge-like position. This modification adds an extra glute activation component to the exercise.
- If you want to focus on the shoulders, you can incorporate an overhead press into the swing movement. As you swing the kettlebell up, press it overhead, fully extending your arms. This modification engages the deltoids and trapezius muscles to a greater extent.
Remember, proper form and technique are crucial when performing any exercise variation. Maintain a neutral spine, engage your core throughout the movement, and choose a weight that allows you to execute the swings with control and good form.
Now that you understand the muscle groups targeted during kettlebell swings and have learned how to modify the exercise for emphasis, you can customize your workouts to achieve your fitness goals more effectively.
| Muscle Group | Primary Role |
|---|---|
| Glutes | Generate power and explosiveness in the swing motion. |
| Hamstrings | Work in synergy with the glutes to extend the hips and propel the kettlebell forward. |
| Core | Stabilize the spine and maintain proper form throughout the swing. |
| Shoulders | Control and guide the kettlebell’s trajectory during the swing. |
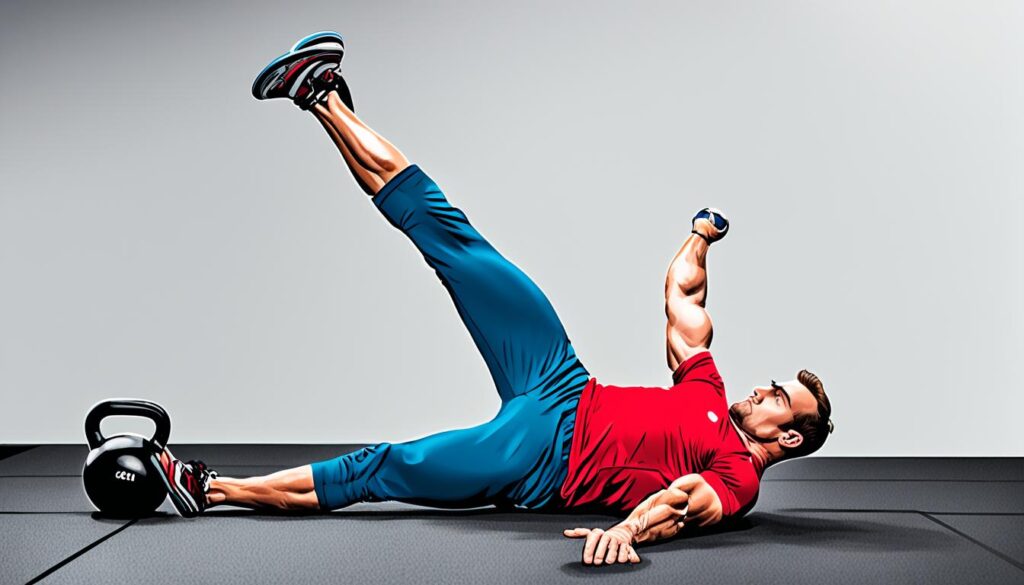

Advanced Variations and Progressions
Looking to take your kettlebell swing to the next level? In this section, I will introduce you to advanced variations and progressions that will challenge your strength and endurance. These dynamic exercises will push your limits and help you achieve new levels of fitness.
1. Single-Arm Swings
In this variation, you will perform the kettlebell swing with one arm, enhancing the intensity and engaging your core even more. Start by gripping the kettlebell with one hand and swing it between your legs, using the power generated from your hips to propel the kettlebell forward. Remember to maintain a neutral spine and switch arms between sets for balanced strength development.
2. Double Kettlebell Swings
If you’re ready to kick it up a notch, try the double kettlebell swing. This challenging variation will require you to use two kettlebells simultaneously, working your upper and lower body in unison. Maintain a firm grip on both kettlebells and follow the same movement pattern as the basic swing. Be prepared for an intense full-body workout!
“Advanced variations and progressions of kettlebell swings allow you to continually challenge yourself and prevent training plateaus.”– Fitness Expert
Remember, before attempting these advanced variations, it’s crucial to master the basic kettlebell swing technique and have a strong foundation of strength and stability. Practice proper form and gradually increase the weight and intensity as you become more comfortable and confident.
By incorporating these advanced variations and progressions into your workout routine, you will continue to see progress and keep your fitness journey exciting and rewarding. Challenge yourself, stay motivated, and enjoy the incredible benefits that kettlebell swings have to offer.
Incorporating Kettlebell Swings with Other Exercises
Incorporating kettlebell swings with other exercises is a great way to enhance your workout routine and target multiple muscle groups. By combining kettlebell swings with exercises such as squats, lunges, and push-ups, you can create a well-rounded and challenging workout that maximizes the benefits of each exercise.
Example Workout Routine:
Here’s an example workout routine that incorporates kettlebell swings with other exercises:
- Warm up with 5 minutes of light cardio.
- Perform 3 sets of kettlebell swings, each consisting of 10-12 reps.
- Immediately after each set of kettlebell swings, transition to squats and perform 12-15 reps.
- Rest for 1-2 minutes and repeat the circuit for a total of 3 rounds.
- After completing the circuit, move on to lunges. Perform 10-12 reps on each leg.
- Rest for 1 minute and repeat the lunges for 2 more sets.
- Finish the workout with push-ups. Perform 8-10 reps, focusing on maintaining proper form.
- Cool down with 5 minutes of stretching.
By incorporating kettlebell swings with squats, lunges, and push-ups, you engage multiple muscle groups, including your glutes, quads, hamstrings, core, and upper body. This combination of exercises not only builds strength but also improves cardiovascular fitness and promotes overall body conditioning.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When performing kettlebell swings, it’s crucial to prioritize safety to prevent injuries and maximize the effectiveness of your workouts. Unfortunately, many people make common mistakes that can compromise their safety and hinder their progress. By being aware of these errors and learning how to correct them, you can ensure a safer and more efficient kettlebell swing training experience.
Avoiding proper warm-up and cooldown
One of the most common mistakes is neglecting to warm up and cool down before and after your kettlebell swing workouts. Warming up helps prepare your muscles by increasing blood flow and range of motion, reducing the risk of strains or pulls. Cooling down, on the other hand, allows your body to recover gradually and promotes flexibility. Make sure to incorporate dynamic stretches and light cardio exercises, such as jogging or jumping jacks, into your warm-up routine. For your cooldown, focus on static stretching and deep breathing exercises to relax your muscles and promote recovery.
Incorrect grip and hand placement
An improper grip and hand placement can compromise your control and stability during kettlebell swings. To avoid this mistake, make sure to grip the kettlebell handle firmly with both hands, keeping your palms facing downwards and fingers wrapped securely around the handle. Ensure that your thumbs are pointing towards your body and that there is no excessive tension in your grip. This grip will provide you with better control, reducing the risk of the kettlebell slipping from your hands.
Overarching or rounding the back
The position of your back plays a vital role in maintaining proper form and preventing injury during kettlebell swings. Overarching or rounding your back can place unnecessary strain on your spine and increase the risk of lower back pain. Instead, focus on maintaining a neutral spine throughout the exercise. Engage your core muscles to stabilize your spine and avoid excessive forward or backward leaning. Keeping your spine aligned will distribute the load evenly and protect your back from potential injuries.
Using excessive weight
Using a weight that is too heavy for your current strength level is a common mistake that can lead to poor form and increased risk of injury. It’s important to start with a weight that you can comfortably handle while maintaining proper technique. Gradually increase the weight as your strength improves and your form remains stable. This progressive approach will allow you to build strength safely and effectively.
Lacking hip and glute engagement
Kettlebell swings are primarily driven by the power generated from your hips and glutes. Failure to engage these muscles properly can result in a loss of power, inefficient movement, and potential strain on other muscle groups. To avoid this mistake, focus on initiating the swing by forcefully contracting your glutes and driving your hips forward. This explosive hip extension will generate power and momentum, allowing for a more effective and safer kettlebell swing.
The following table summarizes these common mistakes to avoid:
| Mistake | Impact | Correction |
|---|---|---|
| Neglecting warm-up and cooldown | Increased risk of injury, limited flexibility | Incorporate dynamic warm-up and static cooldown exercises |
| Incorrect grip and hand placement | Lack of control and stability | Grip kettlebell firmly, thumbs pointing towards body |
| Overarching or rounding the back | Strain on the spine, increased risk of back pain | Maintain a neutral spine, engage core muscles |
| Using excessive weight | Poor form, increased risk of injury | Start with manageable weight, gradually increase as strength improves |
| Lacking hip and glute engagement | Loss of power, inefficient movement | Focus on forcefully contracting glutes and driving hips forward |
By avoiding these common mistakes and focusing on proper technique and safety measures, you can make the most out of your kettlebell swing workouts. Stay mindful of your form, listen to your body, and progress at a pace that is appropriate for your fitness level. Remember, safety should always be a priority to achieve optimal results while minimizing the risk of injury.
Conclusion
Throughout this article, I have highlighted the incredible benefits of kettlebell swings and emphasized the importance of proper form and technique. By integrating this dynamic exercise into your fitness routine, you can experience improvements in strength, cardiovascular endurance, core stability, and calorie burning.
Remember, when performing kettlebell swings, it’s crucial to maintain a neutral spine, engage your hips and glutes, and follow the correct movement pattern. This will not only maximize the effectiveness of the exercise but also minimize the risk of injury.
I encourage you to start with a weight that is appropriate for your fitness level and gradually increase it as you become more proficient. You can also target specific muscle groups by making modifications to the exercise.
Incorporating kettlebell swings with other exercises, such as squats, lunges, and push-ups, can create a well-rounded and challenging workout. By utilizing advanced variations and progressions, you can further challenge yourself and keep your workouts engaging.
In conclusion, kettlebell swings are a versatile and effective exercise that can benefit individuals of all fitness levels. By incorporating them into your workouts, you can achieve improved strength, endurance, and overall health. So why wait? Grab a kettlebell and start swinging your way to a fitter and stronger body.
FAQ
What are kettlebell swings?
Kettlebell swings are a dynamic exercise that involves swinging a kettlebell between the legs and up to chest level. They are a powerful full-body movement that primarily targets the glutes, hamstrings, core, and shoulders.
Why are kettlebell swings beneficial for workouts?
Kettlebell swings offer numerous benefits for your workouts. They help build strength and power, increase cardiovascular endurance, improve core stability, and burn calories. Additionally, they engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously, making them a time-efficient exercise.
What is the proper technique for performing kettlebell swings?
To execute kettlebell swings properly, start with a shoulder-width stance, gripping the kettlebell with both hands. Initiate the movement by hinging at the hips, maintaining a neutral spine, and driving the kettlebell forward using the hips and glutes. Fully extend the hips to generate power and control the swing with a strong core.
How can I integrate kettlebell swings into my workouts?
You can incorporate kettlebell swings into your workouts by adding them as a standalone exercise or combining them with other exercises such as squats, lunges, and push-ups. You can also structure your workouts in circuits or intervals to increase the intensity and challenge.
How do I select the appropriate kettlebell weight for beginners?
For beginners, it is recommended to start with a lighter kettlebell weight to focus on developing proper form and technique. A weight that allows you to perform 10-15 reps with good control and without compromising form is a good starting point. As you become more proficient, gradually increase the weight to challenge yourself.
Which muscle groups does the kettlebell swing primarily target?
The kettlebell swing primarily targets the glutes, hamstrings, core, and shoulders. The explosive hip extension and full-body engagement make it an effective exercise for developing strength and power in these muscle groups.
Are there advanced variations and progressions for kettlebell swings?
Yes, once you have mastered the basic kettlebell swing, you can progress to advanced variations such as single-arm swings, double kettlebell swings, or adding other exercises like a press or glute bridge. These variations increase the challenge and provide additional benefits.
How can I combine kettlebell swings with other exercises in my workout routine?
You can combine kettlebell swings with exercises like squats, lunges, and push-ups to create a comprehensive workout routine. For example, you can perform a set of kettlebell swings, followed by a set of squats, then lunges, and finish off with push-ups. This combination targets different muscle groups and keeps your workouts challenging and effective.
What are common mistakes to avoid when performing kettlebell swings?
Common mistakes when performing kettlebell swings include using too much upper body strength, rounding the back, using improper grip, and not engaging the glutes. It is important to focus on using the hips and glutes to generate power and maintaining a neutral spine throughout the movement.
How do I conclude my workout routine with kettlebell swings?
To conclude your workout routine with kettlebell swings, gradually decrease the intensity and volume. Perform a few sets of kettlebell swings with a lighter weight and focus on maintaining proper form. This allows for a cool-down period and helps prevent excessive fatigue or injury.
Beginner’s Guide: dumbbell workouts
Did you know that incorporating dumbbell workouts into your fitness routine can help you build strength and tone your muscles? Whether you’re new to working out or looking to switch up your current routine, dumbbell exercises offer a versatile and effective way to achieve your fitness goals.
Key Takeaways:
- Dumbbell workouts provide a versatile and effective way to build strength and tone muscles.
- They are suitable for beginners and can be performed at home.
- Using dumbbells allows you to target specific muscle groups with proper form and control.
- You can engage both your upper and lower body with a wide range of dumbbell exercises.
- Progression and proper form are crucial for maximizing the benefits of dumbbell workouts.
Why Choose Dumbbell Workouts?
Before we dive into specific exercises, let’s explore why dumbbell workouts are an excellent choice for beginners. Dumbbells provide stability and control, allowing you to target specific muscles with proper form. They offer a wide range of exercises that engage both the upper and lower body, making them a versatile tool for a full-body workout.
With dumbbell workouts, you have the flexibility to adjust the weight according to your fitness level and goals. Whether you’re aiming to build strength, increase muscular endurance, or tone your muscles, dumbbells can be tailored to suit your needs.
Dumbbell workouts also offer unilateral training, which means each side of your body works independently. This helps to correct muscle imbalances and improve overall coordination and stability. Additionally, dumbbells allow for a greater range of motion compared to some machines, enabling you to work the muscles through their full potential.
Another benefit of dumbbell exercises is their convenience. You can perform dumbbell workouts at home or in the gym, making them accessible and suitable for individuals with busy schedules. They take up minimal space and are relatively affordable compared to other workout equipment.
Whether your goal is to increase muscle mass, improve functional strength, or boost overall fitness, incorporating dumbbell workouts into your routine can help you achieve your desired results.
“Dumbbell workouts offer a versatile and effective way to target different muscle groups and achieve your fitness goals.”
| Benefits of Dumbbell Workouts |
|---|
| Target specific muscles with proper form |
| Versatile tool for a full-body workout |
| Adjustable weight for different fitness levels and goals |
| Unilateral training improves muscle balance and coordination |
| Allows for a greater range of motion |
| Convenient and accessible |
Choosing the Right Dumbbells for Your Dumbbell Workouts
Before you dive into your dumbbell workouts, it’s crucial to choose the right set of dumbbells that suits your fitness level. The weight of your dumbbells will determine the intensity of your exercises and the effectiveness of your training. Here are some key factors to consider when selecting your dumbbells:
- Fitness Level: Assess your current strength and endurance to determine the appropriate weight range for your dumbbells. Beginners typically start with lighter weights, while more advanced individuals may require heavier options.
- Exercise Variety: Consider the wide range of exercises you plan to incorporate into your workouts. Ensure that your dumbbells can support both upper body and leg exercises, as these will be essential for a complete and balanced routine.
- Progression: It’s important to choose dumbbells that allow room for growth. As you get stronger and more comfortable with your workouts, you’ll want to increase the weight of your dumbbells to challenge your muscles and continue making progress.
Once you’ve selected the appropriate weight range for your dumbbells, it’s time to get started! However, before you jump into your exercises, it’s essential to pay attention to proper form and safety precautions.
Remember, using the correct form during exercises helps target the intended muscles effectively and reduces the risk of injuries.
Proper form involves maintaining proper body alignment, controlling the movement, and engaging the targeted muscle groups. Start with lighter weights and focus on mastering the proper technique before progressing to heavier loads.
To ensure safety during your dumbbell workouts, consider the following tips:
- Warm-up: Always begin your workout with a proper warm-up to prepare your muscles and joints for the exercises ahead. This can include light cardio exercises, dynamic stretching, or specific mobility drills.
- Start Slow: Begin with lighter weights and gradually increase the load as you build strength and confidence. Avoid lifting weights that exceed your capabilities, as this can lead to injuries.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to any pain or discomfort during your workouts. If something doesn’t feel right, stop the exercise and seek guidance from a fitness professional or trainer.
- Breathe Properly: Focus on proper breathing techniques throughout your exercises. Inhale during the eccentric phase (lowering or stretching) and exhale during the concentric phase (lifting or contracting) of each movement.
- Use a Spotter (If Needed): If you’re lifting heavy weights or performing exercises that require assistance, it’s advisable to have a spotter to ensure your safety and provide support if necessary.
By selecting the right dumbbells and adopting proper form and safety precautions, you’ll be well on your way to maximizing the effectiveness of your dumbbell workouts and achieving your fitness goals.
Recommended Dumbbell Weights for Beginners |
Recommended Dumbbell Weights for Intermediate/Advanced |
|---|---|
|
|
Dumbbell Exercises for the Upper Body
In this section, I will introduce a variety of dumbbell exercises that specifically target the muscles in your upper body. It’s important to incorporate these exercises into your routine to build strength and tone your arms, chest, back, and shoulders.
Here are some effective dumbbell exercises for your upper body:
- Bicep Curls: Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart, holding a dumbbell in each hand. Keep your back straight and curl the dumbbells up towards your shoulders, squeezing your biceps at the top. Lower the dumbbells back down and repeat for the desired number of repetitions.
- Shoulder Presses: Begin by standing with your feet shoulder-width apart, holding a dumbbell in each hand. Bring the dumbbells up to your shoulders, then press them overhead until your arms are fully extended. Lower the dumbbells back down to shoulder level and repeat.
- Push-Ups: Start in a plank position with your hands slightly wider than shoulder-width apart. Place your dumbbells parallel to each other on the floor, grip the handles, and perform push-ups while maintaining proper form.
- Overhead Tricep Extensions: Stand with your feet hip-width apart, holding a dumbbell with both hands. Extend the dumbbell overhead, keeping your elbows close to your head. Slowly lower the dumbbell behind your head by bending your elbows, then extend your arms back up to the starting position.
- Bent-Over Rows: Stand with your feet hip-width apart, holding a dumbbell in each hand. Hinge forward from your hips, keeping your back flat, and let your arms hang down towards the floor. Pull the dumbbells up towards your chest, squeezing your shoulder blades together, then lower them back down.
Remember to start with lighter weights and gradually increase the resistance as you get stronger. Proper form is essential for these exercises to prevent injury and ensure maximum effectiveness. Focus on maintaining control throughout each movement and engaging the targeted muscles.
Here’s an example of a table showcasing the recommended sets and repetitions for each exercise:
| Exercise | Sets | Repetitions |
|---|---|---|
| Bicep Curls | 3 | 10-12 |
| Shoulder Presses | 3 | 8-10 |
| Push-Ups | 3 | 12-15 |
| Overhead Tricep Extensions | 3 | 10-12 |
| Bent-Over Rows | 3 | 8-10 |
Now that you’re familiar with these dumbbell exercises for the upper body, you can create a well-rounded workout routine that targets all the major muscle groups in your upper body. Stay consistent and gradually increase the weights to continue challenging yourself and achieving your fitness goals.
Dumbbell Exercises for the Legs
Strong and sculpted legs are essential for overall strength and stability.
When it comes to leg exercises, dumbbells offer a versatile way to target your lower body muscles and achieve your fitness goals. Incorporating dumbbell exercises into your leg workout routine can help you build lower body strength, improve your balance, and increase your overall athletic performance. In this section, I will introduce you to a range of effective leg exercises using dumbbells, including squats, lunges, and deadlifts.
Squats
One of the most popular leg exercises, squats are a compound movement that targets multiple muscle groups in your lower body, including your quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and calves. To perform dumbbell squats, follow these steps:
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart, holding a dumbbell in each hand at your sides.
- Engage your core and initiate the movement by bending at the hips and knees, as if sitting back into a chair.
- Lower your body until your thighs are parallel to the ground or slightly below, keeping your chest upright and your knees in line with your toes.
- Push through your heels to return to the starting position, fully extending your hips and knees.
Perform 3 sets of 10-12 reps, gradually increasing the weight as you get stronger. Rest for 60-90 seconds between sets to allow for recovery.
Lunges
Lunges are another effective dumbbell exercise that targets your quads, hamstrings, glutes, and calves, while also engaging your core for stability. Here’s how to perform dumbbell lunges:
- Stand with your feet hip-width apart, holding a dumbbell in each hand at your sides.
- Take a step forward with your right foot, keeping your upper body straight and core engaged.
- Bend both knees to lower your body until your front thigh is parallel to the ground, and your back knee is hovering just above the floor.
- Push through your front heel to return to the starting position, while maintaining control and balance.
Complete 3 sets of 10-12 reps on each leg, gradually increasing the weight as you progress. Rest for 60-90 seconds between sets.
Deadlifts
Deadlifts primarily target your hamstrings, glutes, and lower back muscles, making them an excellent exercise for overall leg and posterior chain development. Incorporating dumbbells into the deadlift movement adds an extra challenge and allows for more range of motion. Here’s how to perform dumbbell deadlifts:
- Stand with your feet hip-width apart, holding a dumbbell in each hand in front of your thighs.
- Hinge at your hips, keeping your back straight, and lower the dumbbells toward the ground.
- Engage your hamstrings and glutes to lift the dumbbells back up to the starting position, pushing your hips forward as you stand tall.
Perform 3 sets of 10-12 reps, gradually increasing the weight as you build strength. Rest for 60-90 seconds between sets.
By incorporating these dumbbell exercises into your leg workout routine, you’ll be able to develop strong and toned legs, improve your functional strength, and enhance your overall fitness level. Remember to start with lighter weights and focus on proper form to prevent injuries and get the most out of each exercise.
Combining Upper Body and Leg Exercises
To maximize your workout and achieve a more balanced physique, it’s important to incorporate both upper body and leg exercises into your routine. By engaging multiple muscle groups simultaneously, you’ll boost calorie burn and enhance overall strength and conditioning. To help you get started, I’ve provided sample workout plans and tips for efficient training.
Sample Workout Plan:
If you’re new to combining upper body and leg exercises, it’s essential to start with a plan that gradually increases in intensity. Here’s a sample workout routine to help you get started:
| Exercise | Sets | Repetitions |
|---|---|---|
| Dumbbell Squats | 3 | 12-15 |
| Push-ups | 3 | 10-12 |
| Dumbbell Lunges | 3 | 12-15 |
| Dumbbell Shoulder Presses | 3 | 10-12 |
| Dumbbell Deadlifts | 3 | 12-15 |
| Tricep Dips | 3 | 10-12 |
| Plank | 3 | 30-45 seconds |
Note: These are general recommendations, and you should adjust the weights and repetitions based on your fitness level. Rest for 1-2 minutes between sets to allow for recovery.
Tips for Efficient Training:
- Start with a warm-up: Prior to your combined upper body and leg workout, perform dynamic stretching exercises or light cardio for 5-10 minutes to increase blood flow and loosen up your muscles.
- Alternate between upper body and leg exercises: This ensures that one muscle group has time to recover while you work on another, allowing you to maintain intensity throughout your workout.
- Focus on proper form: Proper technique is crucial for maximizing results and reducing the risk of injury. Pay attention to your posture, engage your core, and use controlled movements throughout each exercise.
- Progress gradually: As you get stronger, gradually increase the weight, repetitions, or sets to continue challenging your muscles and promote progress.
- Listen to your body: If you experience pain or discomfort during any exercise, stop immediately and consult with a fitness professional or healthcare provider.
By incorporating a variety of upper body and leg exercises into your routine and following these tips, you’ll optimize your workout and achieve a well-rounded physique. Remember, consistency is key, so strive to make exercise a regular part of your lifestyle.
Dumbbell Workouts vs. Other Equipment
Wondering how dumbbell workouts compare to other fitness equipment? When it comes to targeting specific muscles and achieving functional strength, dumbbells offer several advantages over machines, resistance bands, and bodyweight exercises.
Dumbbells allow for a greater range of motion and flexibility compared to machines, which often restrict movement to predetermined pathways. This freedom of movement engages stabilizer muscles and promotes better overall muscular development.
Resistance bands are effective for resistance training, but they do not provide the same level of resistance as dumbbells. Dumbbells allow you to gradually increase weight as you get stronger, providing progressive overload for continued muscle growth and development.
Bodyweight exercises are excellent for building strength and endurance, but they may not provide enough resistance to continually challenge your muscles. Dumbbells, on the other hand, can be easily adjusted to suit your fitness level, ensuring consistent progress over time.
“Dumbbells offer a versatile and convenient way to target specific muscles and achieve a well-rounded, effective workout.”
Additionally, dumbbells offer a wide variety of exercises that engage both your upper body and legs, making them a versatile tool for a full-body workout. By incorporating dumbbell exercises into your routine, you can effectively target your chest, back, arms, shoulders, and legs with a single piece of equipment.
Table: Comparison of Dumbbells, Machines, Resistance Bands, and Bodyweight Exercises
| Dumbbells | Machines | Resistance Bands | Bodyweight Exercises |
|---|---|---|---|
| Allow freedom of movement | Restricted range of motion | Limited resistance | Varies depending on exercise |
| Adjustable weight for progressive overload | Fixed weight | Low to moderate resistance | Depends on body weight |
| Engage stabilizer muscles | Isolate specific muscles | Minimal stabilizer engagement | Varies depending on exercise |
| Target multiple muscle groups | Target specific muscle groups | Varies depending on exercise | Varies depending on exercise |
Overall, dumbbells offer a versatile and convenient way to target specific muscles and achieve a well-rounded, effective workout. Whether you’re focusing on upper body exercises or leg exercises, incorporating dumbbells into your routine can help you reach your fitness goals.
Close Look at Proper Form and Technique
Maintaining proper form and technique is crucial when performing dumbbell workouts. Not only does it help you get the most out of your exercises, but it also minimizes the risk of injuries. In this section, I will break down the key elements of proper form for various exercises, providing you with essential tips for grip, body alignment, and breathing. By following these guidelines, you’ll ensure that each exercise is performed correctly, leading to optimal results.
Proper Grip
When holding dumbbells, it’s important to maintain a secure grip to prevent accidents or dropping weights. Follow these steps to ensure a proper grip:
- Place the dumbbells in the palms of your hands, wrapping your fingers around the handles.
- Keep your fingers relaxed yet firm, with the dumbbells resting on the base of your fingers and the pads of your palms.
- Avoid gripping the dumbbells too tightly, as this can strain your wrists and forearm muscles.
Body Alignment
Correct body alignment is crucial for targeting the intended muscle groups and preventing strain on other areas of your body. Focus on maintaining the following alignment during your dumbbell workouts:
- Stand with your feet hip-width apart, ensuring a stable base.
- Engage your core muscles by pulling your belly button towards your spine.
- Keep your shoulders relaxed and down, away from your ears.
- Maintain a neutral spine by avoiding excessive arching or rounding.
Breathing Technique
Proper breathing technique enhances your performance and helps stabilize your body during dumbbell exercises. Follow these breathing guidelines:
Exhale during exertion: When lifting or pushing the dumbbells, exhale fully, contracting your core muscles.
Inhale during relaxation: As you lower the dumbbells or return to the starting position, inhale slowly and deeply.
Remember, breathing plays a crucial role in maximizing your strength and maintaining stability throughout the movements.
By paying close attention to your grip, body alignment, and breathing, you’ll perform dumbbell exercises with proper form and technique. Practicing these fundamentals will not only enhance your results but also reduce the risk of injury. Now, let’s dive into the specific exercises and techniques you can incorporate into your dumbbell workouts to target your upper body and leg muscles.
Progressing in Dumbbell Workouts
As you gain confidence and strength in your dumbbell workouts, it’s important to continually challenge yourself and strive for progress. Fortunately, there are several strategies you can implement to take your workouts to the next level and continue seeing results.
- Add Weights: One effective way to increase the difficulty of your exercises is to gradually add more weight to your dumbbells. Start with a weight that is challenging but manageable, and as you become stronger, gradually increase the weight to continue challenging your muscles.
- Increase Repetitions: Another way to progress in your dumbbell workouts is to gradually increase the number of repetitions you perform for each exercise. This will help build endurance and push your muscles to work harder.
- Try Variations: To prevent plateaus and keep your workouts interesting, incorporate variations of your favorite dumbbell exercises. This could include performing the exercise at a different angle, changing the grip, or trying unilateral movements to target specific muscles or challenge your balance.
Remember, it’s essential to listen to your body and progress at a pace that feels comfortable and sustainable for you. Pushing yourself too hard without allowing for proper rest and recovery can increase the risk of injury.
“Continually challenging yourself in dumbbell workouts is key to achieving progress and avoiding plateaus.”
Sample Progression Plan
| Exercise | Starting Weight | Progression |
|---|---|---|
| Dumbbell Bicep Curls | 10 lbs | Increase weight by 2 lbs every two weeks |
| Dumbbell Shoulder Press | 15 lbs | Add an extra set every week |
| Dumbbell Lunges | 20 lbs | Increase reps by 2 every week |
By following a well-rounded progression plan and consistently challenging yourself, you’ll continue to see improvements in your strength, endurance, and overall fitness level. Stay dedicated, stay focused, and enjoy the journey of becoming the best version of yourself!
Overcoming Common Challenges
In any fitness journey, there are inevitable challenges that may arise. As you embark on your dumbbell workouts, it’s important to be prepared for these obstacles and have strategies in place to overcome them. Here are some common challenges that beginners often face and practical solutions to help you stay on track toward your fitness goals.
Finding Motivation
Maintaining motivation can be tough, especially when you’re just starting out. It’s natural to have ups and downs, but there are ways to stay motivated throughout your dumbbell workouts:
- Set specific and achievable goals to keep yourself focused.
- Find a workout buddy or join a fitness community for support and accountability.
- Try different exercises and routines to keep your workouts interesting and avoid monotony.
- Reward yourself for reaching milestones and staying consistent.
Overcoming Plateaus
Plateaus can happen when your progress slows down or comes to a halt. To overcome plateaus in your dumbbell workouts, consider these strategies:
- Increase the intensity of your exercises by adding more weight or incorporating advanced variations.
- Implement circuit training or superset workouts to challenge your muscles in new ways.
- Focus on progressive overload, gradually increasing the volume or difficulty of your workouts.
- Take occasional rest days to allow for recovery and prevent burnout.
“The difference between a successful person and others is not a lack of strength, not a lack of knowledge, but rather a lack of will.” – Vince Lombardi
Dealing with Muscle Soreness
Muscle soreness is a common side effect of intense workouts, but it shouldn’t derail your progress. Here are some tips for alleviating and managing muscle soreness:
- Warm up properly before each workout to increase blood flow and prepare your muscles.
- Stretch after your workouts to improve flexibility and reduce muscle tightness.
- Use foam rollers or massage tools to release tension and relieve soreness.
- Stay hydrated and fuel your body with nutritious foods to aid in recovery.
Remember, overcoming challenges is an essential part of any fitness journey. By staying motivated, pushing through plateaus, and taking care of your body, you’ll be able to overcome common obstacles and continue progressing in your dumbbell workouts.

| Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|
| Finding Motivation | Set specific goals, find a workout buddy, try new exercises, reward yourself |
| Overcoming Plateaus | Increase intensity, implement circuit training, focus on progressive overload, take rest days |
| Dealing with Muscle Soreness | Warm up properly, stretch, use foam rollers, stay hydrated |
Tracking Progress and Staying Consistent
Consistency and progress tracking are vital aspects of maintaining long-term success in your dumbbell workouts. To ensure you stay motivated and on track, it’s essential to set realistic goals, track your exercises, and hold yourself accountable. Let’s delve into how you can effectively monitor your progress and maintain consistency in your fitness routine.
Setting Realistic Goals
When it comes to dumbbell workouts, it’s crucial to set achievable goals that align with your abilities and aspirations. Take the time to identify specific targets for your upper body and leg exercises. Whether it’s increasing the weight you lift, the number of reps you perform, or improving your form, setting realistic goals will help you stay focused and motivated throughout your fitness journey.
Tracking Your Workouts
An effective way of measuring your progress is by keeping a workout journal or using a mobile fitness app. Track the exercises you perform, the weights used, the number of repetitions completed, and any observations or comments you have. This record will enable you to identify patterns, track improvements, and make informed decisions on how to progress in your dumbbell workouts.
Remember, progress is not always linear. There may be days when you feel stronger and days when you feel challenged. Embrace the process and trust that consistency will yield results over time.
Creating a Workout Schedule
Staying consistent with your dumbbell workouts requires developing a regular exercise routine. Set aside dedicated time each week for your upper body and leg exercises. By treating these workouts as non-negotiable appointments, you’re more likely to follow through and stay committed to your fitness goals.
Let’s take a look at an example of a sample workout schedule:
| Day | Upper Body Exercises | Leg Exercises |
|---|---|---|
| Monday | Dumbbell Rows, Shoulder Presses, Tricep Kickbacks | Goblet Squats, Lunges, Calf Raises |
| Wednesday | Bicep Curls, Chest Presses, Arnold Presses | Deadlifts, Bulgarian Split Squats, Side Lunges |
| Friday | Push-ups, Hammer Curls, Bent-Over Flyes | Step-ups, Glute Bridges, Leg Presses |
Feel free to adjust this schedule based on your preference and availability. Remember to incorporate rest days to allow your muscles to recover and grow.
Celebrating Milestones
As you progress in your dumbbell workouts, make sure to celebrate your successes along the way. When you reach a significant milestone, such as increasing your weight or completing a challenging exercise, reward yourself with something you enjoy. Recognizing your achievements will keep you motivated and eager to continue pushing yourself in your fitness journey.
By setting realistic goals, tracking your workouts, creating a consistent workout schedule, and celebrating milestones, you’ll be well on your way to achieving long-term success with your dumbbell workouts.
Conclusion
This beginner’s guide to dumbbell workouts provides you with the tools and knowledge to start your journey toward building strength and transforming your fitness routine. Incorporating dumbbell exercises for your upper body and legs will help you achieve a balanced physique and improve your overall fitness level.
Remember to start with proper form to ensure maximum effectiveness and reduce the risk of injuries. As you progress, challenge yourself by increasing weights or repetitions, and try different variations of exercises to keep your workouts engaging and effective.
Consistency is key in achieving long-term results. Stick to a regular workout schedule and track your progress to stay motivated and accountable. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced fitness enthusiast, dumbbell workouts offer a versatile and effective way to achieve your fitness goals.
FAQ
Why should I choose dumbbell workouts?
Dumbbell workouts are a great choice for beginners because they provide stability and control while targeting specific muscles with proper form. They also offer a wide range of exercises that engage both your upper and lower body, making them a versatile tool for a full-body workout.
How do I choose the right dumbbells for my fitness level?
When choosing dumbbells, consider factors such as your current strength level and exercise goals. Start with a weight that challenges you but allows you to maintain proper form. You can gradually increase the weight as you get stronger. It’s important to prioritize proper form and safety to prevent injuries.
What are some dumbbell exercises for the upper body?
There are various dumbbell exercises that target the upper body, including bicep curls, shoulder presses, and chest presses. These exercises help tone your arms, chest, back, and shoulders, providing you with a well-rounded upper body workout.
Which dumbbell exercises are good for the legs?
Dumbbell exercises are effective for strengthening and toning the legs. Some examples include squats, lunges, and deadlifts. These exercises work your quads, hamstrings, glutes, and calves, helping you build lower body strength and improve your balance.
Can I combine upper body and leg exercises in my dumbbell workouts?
Absolutely! Combining upper body and leg exercises in your dumbbell workouts allows you to engage multiple muscle groups and achieve a more balanced workout. This can lead to greater calorie burn and overall strength improvement. We’ll provide sample workout plans and tips on how to efficiently incorporate both upper and lower body exercises.
How do dumbbell workouts compare to other fitness equipment?
Dumbbell workouts offer unique benefits compared to machines, resistance bands, and bodyweight exercises. Dumbbells allow you to target specific muscles, provide a greater range of motion, and improve functional strength. They are versatile and can be used for various upper body and leg exercises.
What should I know about proper form and technique in dumbbell workouts?
Maintaining proper form and technique is crucial for maximizing the benefits of dumbbell workouts and preventing injuries. We’ll break down the key elements of proper form for different exercises, including grip, body alignment, and breathing. This section will provide you with the knowledge to perform each exercise correctly for optimal results.
How can I progress in my dumbbell workouts?
As you become more comfortable with dumbbell workouts, it’s important to challenge yourself and continue making progress. We’ll provide strategies for increasing the difficulty of your exercises, such as adding weights, increasing repetitions, or trying variations. This section will guide you on how to adapt your workouts as you get stronger.
What are some common challenges I may face during dumbbell workouts?
In any fitness journey, challenges may arise. This section will address common obstacles beginners face during dumbbell workouts and offer practical solutions. Whether it’s finding motivation, overcoming plateaus, or dealing with muscle soreness, we’ll provide tips to keep you on track toward your goals.
How can I track my progress and maintain consistency in my dumbbell workouts?
Consistency and progress tracking are key to long-term success in any fitness routine. We’ll discuss the importance of setting realistic goals, tracking your workouts, and staying accountable. From creating a workout schedule to celebrating milestones, this section will guide you on how to stay motivated and consistent on your fitness journey.
How can I use dumbbell workouts to transform my fitness routine?
This beginner’s guide to dumbbell workouts has provided you with the tools and knowledge to start your journey toward building strength and transforming your fitness routine. By incorporating dumbbell exercises for your upper body and legs, you’ll achieve a balanced physique and improve your overall fitness level. Remember to start with proper form, progress at your own pace, and stay consistent on your fitness journey.
What You Need to Know About hip thrusts
Did you know that strengthening your glutes can have a significant impact on your overall fitness and performance? One effective exercise that specifically targets and enhances your glutes is the hip thrust. Hip thrusts are not only beneficial for sculpting your lower body, but they also play a crucial role in improving your strength and power.
In this article, I will provide you with a comprehensive guide to hip thrusts. You will learn about the benefits of incorporating hip thrusts into your workout routine, the proper techniques to perform them, and various variations you can try. Additionally, I will share tips for maximizing the effectiveness of your hip thrusts and overcoming common challenges that may arise. By the end of this article, you’ll have all the information you need to confidently integrate hip thrusts into your fitness regimen and strengthen those glutes!
Key Takeaways:
- Hip thrusts are an exercise that targets and strengthens the glute muscles.
- They provide numerous benefits such as improved glute activation, muscle growth, and overall strength.
- Proper technique and form are crucial for effective hip thrusts.
- There are various variations of hip thrusts that can be incorporated into your workouts.
- By following the tips and strategies provided, you can maximize the effectiveness of your hip thrusts and overcome common challenges.
Understanding Hip Thrusts
When it comes to lower body exercises that target and strengthen the glute muscles, hip thrusts are among the most effective. Understanding the mechanics of hip thrusts and their specific benefits for the glutes can help you make the most out of this exercise in your fitness routine.
The Science Behind Hip Thrusts
Hip thrusts are compound exercises that primarily involve hip extension. This movement pattern specifically activates the gluteus maximus, the largest muscle in the gluteal group, while also engaging the hamstrings and quadriceps to a lesser extent.
During a hip thrust, you start by sitting on the ground with your back against a bench or elevated platform. With your feet planted firmly on the ground and your knees bent, you thrust your hips upward, pushing your body into a bridge position. The exercise can be performed with or without additional weight, such as a barbell or dumbbell, to increase the intensity.
A successful hip thrust relies on proper form, including maintaining a neutral spine, activating the glutes throughout the movement, and driving through the heels. When executed correctly, hip thrusts effectively isolate and target the glute muscles, leading to increased strength and improved muscle activation.
The Benefits of Hip Thrusts
Hip thrusts offer a range of benefits that make them a valuable addition to any lower body workout routine.
“Hip thrusts are a compound exercise that directly targets the glutes, making them an excellent choice for anyone looking to strengthen and tone their lower body.”
- Glute Activation: Hip thrusts emphasize the activation of the glute muscles, stimulating growth and enhancing their overall strength.
- Increased Muscle Growth: By targeting the glutes directly, hip thrusts can lead to hypertrophy (muscle growth) in the gluteal muscles, helping to shape and define your rear end.
- Improved Performance: Strong glutes are essential for various functional movements, including running, jumping, and lifting. Hip thrusts can enhance your athletic performance by boosting the power and stability of your lower body.
- Injury Prevention: Strengthening the glutes with hip thrusts can help improve posterior chain stability and alignment, reducing the risk of injury in the lower back, hips, and knees.
Whether your goal is to build a stronger booty, improve your athletic performance, or prevent injuries, incorporating hip thrusts into your routine is a smart choice for overall lower body development.
Benefits of Hip Thrusts
Incorporating hip thrusts into your fitness routine can provide numerous benefits for your glute muscles, muscle growth, strength, and overall athletic performance. Let’s dive into the advantages that hip thrusts offer:
- Glute Activation: Hip thrusts are specifically designed to target and activate the gluteal muscles. By incorporating this exercise into your routine, you can effectively engage and strengthen your glutes, leading to improved muscle tone and definition.
- Muscle Growth: Hip thrusts are a compound exercise that recruits multiple muscle groups, including the glutes, hamstrings, and quadriceps. Performing hip thrusts with progressive overload can stimulate muscle hypertrophy, promoting optimal muscle growth in the lower body.
- Increases in Strength: Hip thrusts are an effective exercise for improving lower body strength. By progressively challenging your muscles with heavier weights over time, you can enhance your strength in hip extension, which translates to improved performance in various movements like squats and deadlifts.
- Enhanced Athletic Performance: Strong glute muscles are essential for athletic performance, as they contribute to power, speed, and agility. Hip thrusts help to develop explosive hip extension, which can enhance your performance in activities such as running, jumping, and sports-specific movements.
Incorporating hip thrusts into your fitness routine can engage your glute muscles, promote muscle growth, increase overall strength, and enhance athletic performance.
In addition to these benefits, hip thrusts can also contribute to improved posture and stability, as they target the posterior chain muscles. Moreover, they can be progressed and modified to cater to individual fitness levels and goals. Whether you are a beginner or an advanced lifter, hip thrusts can be customized to suit your needs.
To further illustrate the benefits of hip thrusts, take a look at the table below, which summarizes the advantages discussed:
| Benefits of Hip Thrusts |
|---|
| Glute Activation |
| Muscle Growth |
| Increases in Strength |
| Enhanced Athletic Performance |
As you can see, hip thrusts offer a range of benefits that can positively impact your fitness journey. In the next section, I will guide you through the proper technique for performing hip thrusts to maximize their effectiveness and ensure safety.
Proper Technique for Hip Thrusts
When performing hip thrusts, it is crucial to focus on proper technique to effectively engage the glute muscles and avoid injury. Follow these step-by-step instructions to ensure you perform hip thrusts with correct form and alignment:
- Set up your equipment: Place a barbell across your hips or hold a dumbbell on your pelvis. Sit on the ground with your back against a bench or a stable elevated surface. Position your feet hip-width apart and flat on the floor.
- Engage your core: Before initiating the movement, engage your core muscles by drawing your belly button toward your spine. This will help stabilize your body throughout the exercise.
- Drive through your heels: Press your heels into the ground and lift your hips off the floor, pushing them upward until your body forms a straight line from your knees to your shoulders. Squeeze your glutes at the top of the movement.
- Lower with control: Lower your hips back down to the starting position, maintaining control and avoiding excessive momentum. Do not let your hips touch the ground between repetitions to keep tension on the glutes.
It’s important to maintain proper form and alignment throughout the entire movement. Here are some tips to ensure you perform hip thrusts correctly:
- Keep your spine neutral: Avoid arching your lower back excessively or rounding your shoulders. Maintain a neutral spine throughout the exercise to protect your lower back and promote effective glute activation.
- Avoid pushing with your toes: Focus on driving through your heels to activate your glutes and hamstrings properly. Pushing with your toes can shift the emphasis to your quadriceps.
- Don’t overextend at the top: While it’s important to fully extend your hips at the top of the movement, avoid hyperextending your back. Maintain control and engage your glutes without overarching your spine.
- Choose the appropriate resistance: Whether using a barbell or dumbbell, select a weight that challenges you without compromising your form. Gradually increase the resistance as you become stronger and more comfortable with the exercise.
By following these guidelines, you can perform hip thrusts with proper technique and maximize the activation of your glute muscles. Remember to start with a weight and variation that suits your fitness level and gradually progress as you build strength and confidence.
Variations of Hip Thrusts
When it comes to hip thrusts, there are a variety of ways to add diversity to your workouts while targeting those glute muscles. In this section, I will explore different variations of hip thrusts that can be incorporated into your training routine. Whether you prefer using bench, dumbbells, or even resistance bands, there’s a variation for everyone.
Bench Hip Thrusts
The bench hip thrust is a popular variation that allows for greater range of motion and increased glute activation. To perform this variation:
- Position your upper back against a bench, with your shoulders in line with the edge of the bench.
- Place your feet flat on the floor, hip-width apart, and your knees bent at a 90-degree angle.
- Hold a barbell across your hips, or you can opt for using dumbbells placed on your hips for added resistance.
- Engage your glutes and drive your hips upward, squeezing your glutes at the top of the movement.
- Lower your hips back down to the starting position and repeat for the desired number of repetitions.
Dumbbell Hip Thrusts
If you prefer using dumbbells or want to target each side of your body individually, dumbbell hip thrusts are a great option. Here’s how to perform this variation:
- Start by sitting on the floor with your upper back resting against a bench or box.
- Hold a dumbbell in each hand, resting them on the tops of your thighs.
- Position your feet flat on the floor, hip-width apart.
- Initiate the movement by driving through your heels and raising your hips until your thighs are parallel to the floor.
- Squeeze your glutes at the top and then lower your hips back down to the starting position.
- Repeat the movement for the desired number of repetitions.
Resistance Band Hip Thrusts
Resistance bands can be a valuable tool to add extra resistance and challenge to your hip thrusts. Here’s how to perform resistance band hip thrusts:
- Place a resistance band just above your knees.
- Position your upper back against a bench or box, with your feet flat on the floor, hip-width apart.
- Drive your hips upward, squeezing your glutes at the top.
- Lower your hips back down and repeat for the desired number of repetitions.
Advanced Variations
If you want to take your hip thrusts to the next level, there are advanced variations that you can incorporate into your routine:
- Single-Leg Hip Thrusts: Perform a traditional hip thrust, but with one leg extended straight out in front of you. This variation provides a greater challenge to your glutes and core stability.
- Hip Thrust Swings: This dynamic variation involves using a kettlebell or dumbbell and performing hip thrusts with an explosive upward movement, similar to a kettlebell swing. It engages more muscles and adds a cardiovascular element to your workouts.
By incorporating these variations into your workout routine, you can keep your glute training exciting and challenging. Explore different options, experiment with variations, and find what works best for you. Remember to always prioritize proper form and listen to your body to avoid any injuries.
Incorporating Hip Thrusts into Your Workout Routine
When it comes to lower body exercises, hip thrusts are a powerful tool for glute activation and overall strength development. In this section, I will guide you on how to effectively incorporate hip thrusts into your workout routine, ensuring optimal results.
The Ideal Frequency, Sets, and Reps
To maximize the benefits of hip thrusts, it’s important to strike a balance between challenging your muscles and allowing them to recover. Aim to perform hip thrusts 2-3 times per week, with at least 48 hours of rest between sessions. This frequency will provide enough stimulus for muscle growth without overtraining.
Tip: Remember, proper form and alignment are crucial for avoiding injuries and optimizing your gains. Be mindful of your positioning and engage your glutes throughout the movement.
When it comes to the number of sets and reps, it depends on your fitness level and goals. Beginners can start with 2-3 sets of 10-12 reps, gradually increasing the intensity as they become more comfortable. Intermediate and advanced individuals can aim for 3-4 sets of 8-10 reps with heavier weights.
Complementary Exercises for Enhanced Results
While hip thrusts alone can provide great benefits, incorporating complementary exercises into your routine can further enhance the activation and development of your glute muscles.
- Lunges: Perform walking lunges or stationary lunges to target your glutes, hamstrings, and quadriceps.
- Deadlifts: Include both conventional and sumo deadlifts to engage your glutes, hamstrings, and lower back.
- Step-ups: Step-ups with dumbbells or barbells help strengthen your glutes, quadriceps, and hamstrings.
- Glute bridges: This exercise complements hip thrusts and targets the glutes and hamstrings effectively.
By incorporating these exercises into your routine, you can create a comprehensive lower body workout that targets multiple muscle groups and promotes balanced strength development.
Remember, consistency and progression are key in achieving results. Gradually increase the weight or intensity of your hip thrusts and complementary exercises over time to continue challenging your muscles and driving progress.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
When it comes to performing hip thrusts, there are several common challenges that individuals may encounter. These challenges can range from muscle soreness to difficulty with specific variations. However, with the right techniques and modifications, it is possible to overcome these obstacles and progress in your hip thrust training.
Muscle Soreness
One of the common challenges associated with hip thrusts is muscle soreness. As the glutes are the primary muscles targeted during this exercise, it is not uncommon to experience soreness in this area. To alleviate muscle soreness, it is important to prioritize proper warm-up and cooldown routines. Additionally, incorporating stretching exercises specific to the glutes can help reduce muscle tension and soreness. Foam rolling and other forms of self-myofascial release techniques can also provide relief by targeting trigger points in the glute muscles.
Difficulty with Variations
Another challenge individuals may face is difficulty with certain variations of hip thrusts. While the basic hip thrust may be manageable, advanced variations like single-leg hip thrusts or hip thrust swings can present a greater challenge. If you find yourself struggling with these variations, it is important to start with modifications that gradually progress towards the full movement. This can include using bodyweight or resistance bands before attempting more challenging variations. Focusing on proper form and technique is crucial to ensure that you are engaging the glutes effectively and avoiding compensations with other muscles.
Modifications and Progressions
Modifications and progressions play a key role in overcoming common challenges related to hip thrusts. By starting with modifications and gradually progressing towards more advanced variations, you can build strength and improve your performance over time. Working with a qualified fitness professional or certified trainer can be beneficial in designing a program that caters to your specific needs and goals. They can provide guidance on appropriate modifications and help you develop a progressive plan that allows for steady improvements in glute strength and overall performance.
Remember, challenges are a natural part of any fitness journey. Embrace them as opportunities for growth and improvement, and don’t be afraid to seek help when needed.
By addressing common challenges such as muscle soreness and difficulty with variations, you can enhance your hip thrust training and optimize glute activation. With proper modifications and progressions, you can overcome these obstacles and continue progressing towards your fitness goals.
Tips for Maximizing Your Hip Thrusts
When it comes to hip thrusts, there are several strategies you can implement to maximize their effectiveness and achieve the best results for your glutes. In this section, I will share some valuable tips and techniques that will help you take your hip thrusts to the next level.
1. Establish a Strong Mind-Muscle Connection
One key to getting the most out of your hip thrusts is to establish a strong mind-muscle connection with your glutes. Focus on contracting and squeezing your glute muscles throughout the entire movement. Visualize them working and engage them intentionally to ensure optimal activation and maximum benefit.
2. Implement Progressive Overload
Progressive overload is crucial for continuous growth and improvement. Gradually increasing the intensity and challenge of your hip thrusts will stimulate muscle growth and strength gains. You can do this by adding weight, increasing repetitions or sets, or progressing to more advanced variations of the exercise.
3. Incorporate Different Tempo Variations
Varying the tempo of your hip thrusts can add an extra challenge and stimulus for your glutes. Try performing slow and controlled repetitions, emphasizing the eccentric (lowering) phase of the movement, or include explosive and powerful thrusts for a more dynamic workout. Experiment with different tempos to keep your muscles guessing and promote greater muscle growth.
4. Ensure Proper Recovery
Recovery plays a vital role in muscle growth and overall performance. After intense hip thrust workouts, give your glutes sufficient time to recover and rebuild. Make sure to incorporate rest days into your training schedule and prioritize adequate sleep, nutrition, and hydration. Taking care of your body will optimize your results and prevent the risk of overtraining or injury.
“To maximize the benefits of hip thrusts, it’s essential to establish a strong mind-muscle connection, implement progressive overload, incorporate different tempo variations, and prioritize proper recovery.”
By following these tips and strategies, you can unlock the full potential of your hip thrusts and make significant progress in strengthening your glutes. Remember, consistency and proper technique are key, so be patient, stay focused, and enjoy the journey to a stronger lower body!
Conclusion
In conclusion, hip thrusts are a highly effective exercise for strengthening the glutes and enhancing lower body workouts. As we have seen throughout this article, hip thrusts target and activate the glute muscles, contributing to muscle growth, improved strength, and enhanced athletic performance.
By performing hip thrusts with proper technique, you can ensure optimal glute activation and minimize the risk of injury. Incorporating variations of hip thrusts such as using a barbell, dumbbells, or resistance bands can help add variety and challenge to your workouts.
I encourage you to include hip thrusts in your fitness routine regularly. Aim to establish a strong mind-muscle connection, progressively overload the muscles, and allow for proper recovery. By doing so, you can maximize the effectiveness of your hip thrusts and achieve greater glute strength and lower body development.
So, whether you are a fitness enthusiast, athlete, or simply looking to tone and strengthen your lower body, don’t overlook the power of hip thrusts. Add this exercise to your repertoire and experience the benefits firsthand!
FAQ
What are hip thrusts?
Hip thrusts are a lower body exercise that primarily targets the glute muscles. It involves lifting your hips off the ground using the strength of your glutes and hips.
What are the benefits of incorporating hip thrusts into my workout?
Hip thrusts offer several benefits including strengthening the glute muscles, improving lower body power and explosiveness, enhancing athletic performance, and helping to prevent injuries.
How do I perform hip thrusts with proper technique?
To perform hip thrusts correctly, start by sitting on the ground with your back against a bench, place a barbell or a dumbbell across your hip crease, and drive through your feet to lift your hips until your body forms a straight line. Engage your glutes, pause at the top, and slowly lower your hips back down.
Can I do variations of hip thrusts?
Yes, there are several variations of hip thrusts that you can incorporate into your workouts. These include using a bench for support, incorporating dumbbells or resistance bands, and performing single-leg hip thrusts or hip thrust swings for added challenge.
How often should I include hip thrusts in my workout routine?
The frequency of hip thrusts in your workout routine will depend on your goals and training program. It is generally recommended to include them 2-3 times per week for optimal glute activation and muscle development.
What are some common challenges when doing hip thrusts and how can I overcome them?
Common challenges when performing hip thrusts include muscle soreness and difficulty with certain variations. To overcome soreness, start with lighter weights and gradually increase the load. For difficulties with variations, modify the exercise or seek guidance from a fitness professional.
How can I maximize the effectiveness of my hip thrusts?
To maximize the effectiveness of your hip thrusts, focus on establishing a strong mind-muscle connection with your glutes, progressively overload by increasing weight or reps over time, vary the tempo of your repetitions, and ensure proper rest and recovery between sessions.
Optimizing power clean
Did you know that the power clean is not only a staple exercise in weightlifting and strength training, but it is also one of the most effective movements for building raw power and explosive strength? Diving deep into the secrets of this exercise can unlock untapped potential in your training regimen.
In this article, I will guide you through the steps and techniques needed to optimize your power clean, enabling you to maximize your strength gains and enhance overall efficiency. By perfecting your form and understanding the key elements of the power clean, you can take your performance to the next level and achieve remarkable results.
Key Takeaways:
- Power clean is a highly effective exercise for building raw power and explosive strength.
- Optimizing your power clean technique can lead to significant increases in strength gains.
- Understanding form and key elements of the power clean is crucial for maximizing efficiency.
- Progressive training and proper incorporation of the power clean into your program are essential for continued improvement.
- By following the strategies outlined in this article, you can unlock your full potential in the power clean and elevate your athletic performance.
Understanding the Power Clean
Before we can optimize the power clean, it’s crucial to have a clear understanding of what this exercise entails and how it can benefit your training. The power clean is a compound movement that targets multiple muscle groups simultaneously, making it a highly effective exercise for building strength and power. By mastering the proper form and technique, you can unlock its potential for hypertrophy and take your training to new heights.
The power clean primarily engages the muscles of the lower body, including the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and calves. Additionally, it activates the muscles of the upper body, such as the trapezius, deltoids, and forearms, to help stabilize the weight during the movement. This comprehensive muscle recruitment makes the power clean an excellent choice for athletes looking to develop explosive power, enhance athletic performance, and promote overall muscular development.
Did You Know? The power clean is a popular exercise among Olympic weightlifters, as it is one of the key lifts in the sport. It requires both strength and technique, making it a challenging but rewarding movement.
Executing the power clean with proper form is essential for reaping its full benefits and avoiding injury. Let’s dive into the key elements of form and technique:
- Starting Position: Begin with your feet shoulder-width apart, gripping the barbell just outside your shins. Your shoulders should be slightly in front of the bar, and your back should be in a neutral position.
- First Pull: Initiate the movement by driving through your legs and extending your hips. As the bar passes your knees, keep it close to your body and maintain a strong, upright posture.
- The Triple Extension: As you reach full extension, explosively jump and shrug the barbell, extending your ankles, knees, and hips simultaneously. This triple extension generates power and momentum, allowing you to lift the barbell to your chest.
- Receiving Position: In the most efficient technique, you should pull your body under the barbell and catch it in a front squat position. Keep your elbows high, chest up, and core engaged to control the weight.
- Stand Up: From the receiving position, drive forcefully through your heels, extending your hips and knees to stand up fully. Maintain control over the weight as you return to the starting position.
Remember, mastering the power clean takes practice and patience. It’s essential to start with lighter weights and gradually increase the load as your form and technique improve. Always prioritize proper form and ensure you are performing the exercise safely to avoid any unnecessary strain or injury.
Hypertrophy and the Power Clean
In addition to its benefits for developing strength and power, the power clean has the potential to promote hypertrophy, or muscle growth. By targeting multiple muscle groups simultaneously and engaging them in a dynamic movement, the power clean creates significant muscular overload, stimulating the body’s adaptive response to build muscle tissue.
However, it’s important to note that the power clean is primarily a power-focused exercise rather than a purely hypertrophy-focused one. The load lifted during a power clean is typically lower than what would be used for hypertrophy training with traditional resistance exercises.
That said, when performed with proper form and technique, the power clean can still contribute to muscle growth, especially in the lower body muscles, such as the quads, hamstrings, and glutes. Additionally, the power clean engages the upper body muscles, including the traps, deltoids, and forearms, which can also benefit from increased muscular development.
It’s worth noting that hypertrophy training typically involves higher repetitions and longer time under tension compared to power clean training. Therefore, if your primary goal is hypertrophy, incorporating the power clean into your training program as a complementary exercise can provide a unique stimulus and enhance overall muscular development.
| Muscle Group | Primary Activation during Power Clean |
|---|---|
| Quadriceps | High |
| Hamstrings | High |
| Glutes | High |
| Trapezius | High |
| Deltoids | Moderate |
| Forearms | Moderate |
Mastering the Power Clean Technique
Perfecting your power clean technique is essential for maximizing its effectiveness and minimizing the risk of injury. As a beginner, it’s crucial to understand the proper form and step-by-step process of performing a power clean. Let’s break it down:
Grip and Set-Up
Start by standing with your feet shoulder-width apart, toes pointing slightly outward. Bend at the knees and hips, lowering your hips towards the floor while keeping your back straight. Place your hands just outside your legs, gripping the bar with an overhand grip. Ensure your shoulders are over the bar and your arms are straight.
First Pull
Begin the lift by extending your legs and driving through your heels. Simultaneously, pull the barbell up, keeping it close to your body. Keep your back flat and engage your core for stability.
Transition and Catch
As the barbell reaches the knee level, rapidly extend your hips, driving your body upward. As you reach full extension, aggressively shrug your shoulders, allowing the momentum to carry the barbell upwards. At this point, pull yourself under the barbell by bending your elbows and rotating your wrists, creating a “shelf” with your shoulders to catch the bar in a front rack position. Keep your upper arms parallel to the ground and your elbows high.
Front Squat and Finish
Once you’ve caught the bar, immediately lower into a front squat position by bending at the knees and hips. Keep your chest up and your elbows high to maintain control of the weight. In the front squat position, stand back up to finish the lift, extending your hips and knees to a fully upright position. Control the descent of the barbell back to the starting position.
Tips for Beginners:
- Start with light weight to focus on mastering technique before progressing to heavier loads.
- Practice each phase of the power clean separately before putting it all together.
- Record yourself performing the power clean to analyze and correct any form issues.
- Seek guidance from a qualified coach or trainer to ensure proper technique and safety.
Remember, the power clean is a complex movement that requires practice and patience. Don’t rush the learning process. Focus on perfecting your form and gradually increasing the weight as you become more comfortable and confident in your technique.
Now that you have a breakdown of the power clean technique, make sure to take your time and focus on each step. Practice regularly to improve your form and gradually increase the weight. With dedication and consistency, you’ll soon master the power clean and unlock its benefits for strength and athleticism.
Building Explosive Power
The power clean is a highly effective exercise for building explosive power in athletes. By harnessing the explosive strength and muscle coordination required to perform the power clean, athletes can enhance their athletic performance, increase their power output, and gain a competitive edge.
The science behind the power clean’s ability to build explosive power lies in its activation of fast-twitch muscle fibers. During the movement, multiple muscle groups, including the quadriceps, glutes, hamstrings, calves, and core, work synergistically to produce a powerful and explosive movement.
Performing the power clean involves a rapid acceleration of the barbell from the floor to the shoulders, requiring a combination of strength, speed, coordination, and technique. This explosive movement recruits a large number of muscle fibers, promoting significant strength gains and improved power output.
When performed correctly, the power clean engages the muscles in a coordinated and efficient manner, training them to generate force rapidly. This translates to improved speed, agility, and power in athletic movements, such as sprinting, jumping, and throwing.
To maximize your power clean’s effectiveness in building explosive power, consider incorporating the following strategies into your training routine:
- Progressive Overload: Gradually increase the weight you lift during power clean training to continuously challenge your muscles and stimulate strength gains.
- Focused Repetition: Practice power clean technique with a focused mindset, ensuring proper form, explosiveness, and coordination.
- Enhanced Speed: Emphasize speed and explosiveness during the lifting phase, aiming to move the weight as quickly as possible while maintaining control.
- Explosive Exercises: Incorporate other explosive exercises, such as plyometrics and Olympic lifts, to complement and enhance the power clean’s effects on power development.
Power clean training is a proven method for developing explosive power, which is essential for athletes in sports such as football, basketball, track and field, and martial arts. It not only improves performance but also reduces the risk of injuries by strengthening the muscles and joints involved in explosive movements.
By consistently incorporating power clean training into your workout routine and progressively challenging yourself, you can experience significant improvements in explosive power and take your athletic performance to new heights.
| Benefits of Power Clean Training: | Strategies for Building Explosive Power: |
|---|---|
|
|
Common Power Clean Mistakes to Avoid
When it comes to the power clean, even the most experienced lifters can fall into bad habits that hinder their progress and compromise their form and safety. To help you optimize your power clean technique, I will highlight some common mistakes to avoid and provide insights on how to correct them.
Mistake 1: Poor Starting Position
One of the most common mistakes in the power clean is starting with a poor position. This often includes rounded shoulders, a hunched back, and improper weight distribution. These errors can compromise your form and make it difficult to generate power efficiently.
Focus on maintaining a tall, upright posture with your shoulders back and chest out. Keep your back flat and engage your core muscles before initiating the lift. Additionally, ensure that your weight is evenly distributed on your feet, with the barbell positioned over your midfoot.
Mistake 2: Neglecting Proper Footwork
Footwork is often overlooked, but it plays a crucial role in your power clean technique. Many lifters fail to establish a solid foundation by either jumping forward or landing with their feet too wide apart.
Instead, concentrate on jumping vertically, driving through your legs, and extending your hips explosively. As you catch the barbell, ensure that your feet land in a stable position, shoulder-width apart, with your toes slightly turned out.
Mistake 3: Using Excessive Arm Pull
Another common mistake is relying too much on your arms to pull the barbell up, rather than utilizing the power generated from your legs and hips. This not only limits your strength potential but also puts unnecessary strain on your upper body.
Focus on initiating the movement with a powerful leg drive and hip extension. As the weight becomes weightless, utilize a quick shrug and pull yourself under the bar, rather than pulling the bar with your arms. This will result in smoother and more efficient power cleans.
Mistake 4: Neglecting the Catch Position
The catch position, also known as the receiving position, is where many lifters make mistakes. Failing to catch the barbell properly can lead to missed lifts, injury, and an overall inefficient power clean.
Ensure that you catch the bar at the front of your shoulders, with your elbows high and parallel to the ground. Your knees should be slightly bent, and your torso should be upright. This position allows for a smooth transition into the final standing position.
Mistake 5: Rushing the Movement
Lastly, rushing through the power clean is a common mistake that compromises both form and safety. Moving too quickly can lead to loss of control, poor technique, and increased risk of injury.
Take your time and focus on each phase of the lift, from the setup to the catch. Remember to explode with power, but maintain control throughout the movement. Quality of movement should always take precedence over speed.
Proper form is essential when performing the power clean. By avoiding these common mistakes, you can optimize your technique, maximize your gains, and reduce the risk of injury. Take the time to refine your form and prioritize safety in every repetition.
Now that you are aware of these common power clean mistakes, you can make the necessary adjustments to ensure optimal form and safety in your workouts. By avoiding these errors and focusing on proper technique, you’ll be on your way to improving your power clean and maximizing your performance.
Variations and Progressions
Once you have mastered the basic power clean, it’s time to explore variations and progressions that can challenge your muscles in new ways. By incorporating different techniques and movements into your training routine, you can continue to develop strength and power while keeping your workouts fresh and exciting.
Here are some variations of the power clean that you can incorporate into your training:
- Hang Power Clean: This variation starts from the hang position, with the barbell resting just above your knees. It targets your posterior chain and explosiveness, providing a different stimulus for muscle growth.
- Single-Leg Power Clean: By performing the power clean on a single leg, you challenge your balance, stability, and overall strength. This variation is beneficial for athletes looking to improve unilateral leg strength and coordination.
- Push Press: The push press combines an overhead press with a power clean. It allows you to lift heavier weights, targeting your shoulders, triceps, and upper body strength.
Remember, when incorporating variations, it’s important to maintain proper form and technique. Start with lighter weights and focus on mastering the movement before progressing to heavier loads. Additionally, consult with a qualified trainer or coach to ensure you are using the correct technique and progressing at a suitable pace.
Progressions
In addition to variations, you can also implement progressions to continuously challenge your muscles and enhance your overall strength. Here are some progressions to consider:
- Increase Weight: Gradually increase the weight of the barbell as you become comfortable with the power clean technique. This progressive overload stimulates muscle growth and increases overall strength.
- Increase Speed: Focus on explosiveness and speed during the power clean. By performing the movement with quick and powerful movements, you can enhance your power output and train your muscles to generate force more efficiently.
- Combine Movements: Incorporate other compound exercises, such as squats or lunges, into your power clean routine. This combination challenges your muscles in different ways, promoting overall strength and muscle development.
Remember, progressions should be implemented gradually and tailored to your individual fitness level and goals. It’s important to listen to your body and make adjustments as needed to avoid overtraining or injury.
By incorporating variations and progressions into your power clean training, you can keep your workouts dynamic and challenging while continuously improving your strength and power. Experiment with different variations and progressions to find what works best for your body and training goals. Remember to always prioritize proper form and technique for safe and effective training.
Incorporating the Power Clean into Your Training Program
To optimize your power clean gains and increase overall strength, it is crucial to understand how to incorporate this exercise into your training program effectively. Here are some recommendations on frequency, sets, and reps, as well as the benefits of combining power clean with other strength-building exercises.
Recommendations for Power Clean Frequency
I recommend incorporating power clean into your training program at least twice a week. This frequency allows for sufficient practice and progression while giving your muscles enough time to recover and adapt to the demands of the exercise.
Setting the Right Sets and Reps
When it comes to power clean, sets and reps can vary depending on your training goals and current fitness level. For strength and power development, I suggest performing 3-5 sets of 3-5 reps with heavy weights, focusing on explosive and controlled movements. If you’re new to power clean or working on technique, start with lighter weights and perform 3-4 sets of 6-8 reps to hone your form and build a solid foundation.
The Benefits of Combining Power Clean with Other Exercises
Power clean is a dynamic full-body exercise that targets multiple muscle groups, making it an excellent addition to your strength training routine. By incorporating power clean into your program, you can improve explosive power, increase overall strength, and enhance muscular coordination and athleticism.
“The power clean is a foundational movement that carries over to many other athletic activities, such as sprinting, jumping, and throwing. It builds strength, power, speed, and coordination when executed properly.”
Combining power clean with exercises like squats, deadlifts, and overhead presses can further enhance the benefits by targeting specific muscle groups and promoting overall strength development. The power clean can also be integrated into HIIT (High-Intensity Interval Training) or circuit training routines for a challenging and efficient full-body workout.
Sample Power Clean Training Program
Here is a sample power clean training program that you can incorporate into your routine:
| Day | Exercise | Sets x Reps |
|---|---|---|
| Monday | Power Clean | 4×4 |
| Wednesday | Squat | 3×8 |
| Friday | Deadlift | 5×5 |
| Saturday | Power Clean | 3×6 |
Remember to gradually increase the weights and adjust the sets and reps as you progress. Listen to your body and rest appropriately between training sessions.

Advanced Techniques for Power Clean Optimization
As you continue on your power clean journey, you have the opportunity to optimize your performance and maximize efficiency by incorporating advanced techniques. These techniques will not only enhance your power clean but also take your strength and athletic prowess to new heights. Let’s explore some dynamic movement cues, breathing techniques, and mental cues that can elevate your power clean capabilities.
Dynamic Movement Cues
Dynamic movement cues are essential for executing a flawless power clean. By focusing on these cues, you can ensure proper form and technique, resulting in increased power output and reduced risk of injury. Here are some key dynamic movement cues to consider:
- Start with a strong and explosive pull from the floor by driving your feet into the ground.
- Keep the barbell close to your body throughout the movement to promote a more efficient transfer of power.
- Engage your core and maintain a tight upper back to optimize power generation.
- Initiate the second pull by forcefully extending your hips and shrugging your shoulders.
- Keep your elbows high and actively pull yourself under the bar during the catch phase.
Breathing Techniques
Proper breathing is often overlooked but plays a crucial role in optimizing your power clean. By coordinating your breath with the movement, you can enhance stability, maintain proper posture, and maximize power generation. Consider the following breathing techniques:
- Take a deep breath and brace your core before initiating the pull. Exhale forcefully as you perform the second pull to generate additional power.
- Inhale as you transition into the catch phase, maintaining a stable core and minimizing any loss of power.
- Exhale as you stand up from the catch position, maintaining a controlled breathing pattern throughout the movement.
Mental Cues
The power clean requires focus, precision, and mental fortitude. Incorporating mental cues into your training can help optimize your performance and efficiency. Consider these mental cues to enhance your power clean:
- Visualize the entire power clean sequence before executing the movement. Imagine yourself executing each phase flawlessly, generating maximum power.
- Stay present and focused throughout the movement, avoiding distractions and maintaining a strong mind-muscle connection.
- Push through any fatigue or discomfort by tapping into your mental strength, reminding yourself of your goals and aspirations.
Incorporating advanced techniques, such as dynamic movement cues, breathing techniques, and mental cues, can significantly optimize your power clean performance and efficiency. By continuously refining your technique and mindset, you can unleash the full power of this dynamic exercise.
Summary
Optimizing your power clean goes beyond perfecting your form and technique; advanced techniques like dynamic movement cues, breathing techniques, and mental cues can take your power clean to the next level. Remember to focus on maintaining proper form, coordinating your breath with the movement, and developing a strong mental game. By incorporating these advanced techniques into your training regimen, you will unlock your full potential and achieve new levels of power and efficiency in your power clean.
Conclusion
In conclusion, optimizing your power clean technique is crucial for unlocking its full potential when it comes to strength and efficiency. By understanding the key principles of the power clean, perfecting your form, and progressively challenging yourself, you can expect to see significant gains in your power clean and overall athletic performance.
One of the key factors in optimizing your power clean is having a strong foundation in technique. By focusing on proper form and executing the movement correctly, you can maximize muscle activation and minimize the risk of injury. Additionally, consistently challenging yourself with appropriate weights and sets will help to increase your strength and power output over time.
It is also important to incorporate the power clean into your overall training program strategically. By combining it with other strength-building exercises and adjusting the frequency, sets, and reps, you can create a well-rounded routine that enhances your overall athletic performance. Remember, consistency and progressive overload are key to continued improvement.
So, whether you are a beginner or an experienced lifter, incorporating the strategies discussed in this article into your power clean training will yield great results. By following the guidelines, refining your technique, and pushing your limits, you can take your power clean to new heights and achieve your strength and efficiency goals. Start implementing these strategies today and witness the transformation in your power clean and overall strength!
FAQ
What is a power clean?
The power clean is a compound exercise that involves lifting a barbell from the floor to the front rack position in a explosive manner. It targets multiple muscle groups, including the legs, hips, back, and shoulders, making it an effective exercise for building overall strength and power.
Can power clean help with muscle hypertrophy?
While the power clean primarily focuses on developing strength and power, it can also contribute to muscle hypertrophy. The explosive nature of the movement places significant stress on the muscles, leading to muscle growth and development over time.
What is the proper form for a power clean?
Proper form is crucial for performing a power clean safely and effectively. Start by standing with your feet hip-width apart, gripping the barbell just outside your thighs. Squat down, keeping your back straight, and explode upward, extending your hips and pulling the barbell towards your shoulders. Catch the barbell in the front rack position with your elbows high and the bar resting on your shoulders.
Is the power clean suitable for beginners?
The power clean can be challenging for beginners due to its technical nature. It is recommended for beginners to start with lighter weights and focus on mastering the proper form and technique before progressing to heavier loads. Working with a qualified coach or trainer can also help beginners learn the movement safely and effectively.
How can the power clean build explosive power?
The power clean is a dynamic exercise that requires explosive power throughout the entire movement. By repeatedly performing power cleans with proper form and progressively increasing the weight, you can improve your ability to generate force quickly, which translates to enhanced explosive power in other activities such as jumping, sprinting, and other explosive movements.
What are some common power clean mistakes to avoid?
Common power clean mistakes include using too much upper body strength, allowing the bar to drift away from the body, not fully extending the hips, and using improper grip width. It is important to focus on maintaining a strong, stable core, keeping the bar path close to the body, fully extending the hips, and using a grip width that allows for a comfortable and secure hold on the barbell.
Are there variations and progressions for the power clean?
Yes, there are various variations and progressions for the power clean that can challenge your muscles in different ways. Some examples include hang power cleans, dumbbell power cleans, and deficit power cleans. These variations can target specific muscle groups and provide new stimulus for continued strength development.
How should I incorporate the power clean into my training program?
The frequency, sets, and reps of power cleans in your training program will depend on your specific goals, fitness level, and overall training volume. It is generally recommended to start with two to three sessions per week, performing three to five sets of five to eight reps. As you progress, you can adjust the intensity and volume based on your individual needs.
What advanced techniques can help optimize the power clean?
Advanced techniques to optimize the power clean include focusing on dynamic movement cues, such as aggressively extending the hips and shrugging the shoulders, utilizing proper breathing techniques to maximize power output, and incorporating mental cues to enhance focus and technique execution. These techniques can help improve efficiency and performance in the power clean.
What You Need to Know About Snatch
Did you know that the snatch lift is not only a staple in Olympic weightlifting, but it is also a highly effective exercise for building upper body power and muscle? This explosive movement engages multiple muscle groups simultaneously, making it a powerhouse exercise for those looking to enhance their athletic performance and achieve hypertrophy.
In this article, I will guide you through the ins and outs of the snatch lift, its technique, and the numerous benefits it brings. We’ll also explore how incorporating split squats and jerks with the snatch can further optimize your muscle development and power output. Whether you’re a seasoned lifter or new to weightlifting, this comprehensive guide will help you unlock the full potential of the snatch lift.
Key Takeaways:
- The snatch lift is a highly effective exercise for building upper body power and muscle.
- It engages multiple muscle groups simultaneously, leading to improved athletic performance and hypertrophy.
- By mastering the technique of the snatch lift, you can optimize muscle activation and power generation.
- Incorporating split squats and jerks with the snatch can further enhance muscle development and power output.
- Proper recovery and injury prevention strategies are crucial when incorporating the snatch lift into your training routine.
Understanding the Snatch Lift
In this section, we will delve into the technique of the snatch lift to gain a deeper understanding of its mechanics and benefits. The snatch is a dynamic and explosive movement that requires proper form and execution to maximize power and engage the targeted muscles effectively.
The snatch lift is a multi-joint exercise that primarily targets the muscles in the upper body, such as the shoulders, back, and arms. It is renowned for its ability to develop exceptional power and explosive strength, making it a staple in many strength and conditioning programs.
The technique of the snatch lift is crucial for optimizing muscle engagement and performance. It involves a series of precise movements that require coordination, balance, and timing. One key aspect of the snatch lift technique is the triple extension of the hips, knees, and ankles, which generates a powerful upward force to propel the barbell overhead.
To perform the snatch lift correctly, proper grip, stance, and body positioning are essential. The grip should be wide, allowing for a secure and stable hold on the barbell. The stance should be shoulder-width apart, with the toes slightly pointed outwards to facilitate a smooth and explosive movement.
During the lift, it is crucial to maintain a strong core and a neutral spine alignment. This ensures proper weight distribution and prevents excessive stress on the lower back. Additionally, focusing on maintaining an upright posture helps engage the muscles of the upper back and shoulders, facilitating a more efficient lift.
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the snatch lift technique:
- Start with the barbell on the floor, with your feet shoulder-width apart and toes slightly pointed outwards.
- Squat down, gripping the barbell with a wide grip.
- Begin the lift by extending your hips, knees, and ankles explosively, driving the barbell upwards.
- As the barbell reaches knee level, quickly transition into an upright posture, shrugging your shoulders and pulling the barbell towards your body.
- Continue the upward movement, pulling the barbell towards your shoulders while transitioning into a partial squat position.
- Once the barbell reaches its maximum height, quickly drop into a deep squat position while extending your arms fully to lock out the lift.
- Stabilize the barbell overhead and hold the position for a brief moment before lowering it back down to the starting position.
The snatch lift requires practice and attention to detail to master the technique. It is recommended to start with lighter weights and gradually increase the load as you become more comfortable and confident with the movement.
Benefits of the Snatch Lift
The snatch lift is a highly effective exercise that offers a multitude of benefits for individuals looking to enhance their fitness routine. By incorporating this compound movement into your training regimen, you can unlock increased power, improved muscle development, and enhanced overall athletic performance.
Let’s explore in more detail the specific benefits of incorporating the snatch lift:
- Increased Power: The snatch lift engages multiple muscle groups simultaneously, including the upper body, core, and lower body. This compound movement requires explosive power to successfully execute the lift, resulting in improved power output and overall strength.
- Improved Muscle Development: The snatch lift targets several major muscle groups, such as the shoulders, back, hips, and legs. This full-body exercise stimulates muscle growth and development, promoting balanced muscle development across various regions of the body.
- Enhanced Athletic Performance: The snatch lift is a functional movement that mimics real-life activities that require power and coordination. By incorporating this exercise into your routine, you can improve your athletic performance in sports that demand explosive power, speed, and agility.
“The snatch lift is a game-changer for overall strength, power, and muscle development. Its ability to engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously makes it one of the most effective exercises for athletes and fitness enthusiasts alike.”
To fully grasp the benefits of the snatch lift, it’s crucial to understand and master the proper technique. Consult with a qualified fitness professional or coach who can guide you through the correct form and provide tailored advice based on your fitness goals.
By incorporating the snatch lift into your fitness routine, you can unleash the tremendous benefits it offers, including increased power, improved muscle development, and enhanced overall athletic performance.
Testimonials
| Name | Occupation | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Emma Green | Olympic Weightlifter | Increased power and explosiveness |
| Mike Anderson | Fitness Enthusiast | Significant muscle gains and improved athletic performance |
| Rebecca Lee | Professional Athlete | Enhanced overall strength and muscle development |
Incorporating Split Squats with the Snatch
When it comes to building muscle and power in the lower body, incorporating split squats alongside the snatch lift can take your training to the next level. Split squats are a highly effective exercise that targets the quadriceps, glutes, and hamstrings, making them an ideal complement to the snatch for overall lower body development.
By combining these two exercises, you are not only engaging multiple muscle groups but also enhancing your power and stability. The split squat requires single-leg strength, which translates into improved balance and control during the snatch, allowing you to lift heavier weights and maximize muscle activation.
Split squats can be performed with bodyweight or added resistance, such as dumbbells or a barbell. To incorporate them into your snatch training, you can either alternate sets between the snatch and split squats or perform them as a superset, moving seamlessly from one exercise to the other.
Here’s an example of how you can structure your snatch and split squat workout:
- Warm up with dynamic stretches and mobility exercises for the hips and ankles.
- Perform a few sets of snatch lifts, focusing on proper technique and power generation.
- Immediately transition into split squats, performing 3-4 sets of 8-12 repetitions on each leg. Use a challenging weight that allows you to maintain proper form.
- Rest for 1-2 minutes between sets to allow for adequate recovery.
- Finish your workout with static stretches for the muscles worked.
By incorporating split squats with the snatch, you are not only building muscle and power in the lower body but also improving your overall athletic performance. The combination of these two exercises will challenge your muscles in new ways, helping you overcome plateaus and reach new levels of strength.
One of the benefits of incorporating split squats with the snatch is their ability to target different muscle groups and movement patterns. While the snatch primarily emphasizes explosive power and coordination, split squats focus on unilateral leg strength and stability. This combination can lead to greater muscle hypertrophy and functional strength in the lower body.
So don’t neglect the power of split squats when it comes to enhancing your snatch training. Incorporate them into your workouts and experience the benefits of increased muscle development and power in the lower body.
Enhancing Hypertrophy with the Snatch
To truly maximize muscle growth and development, incorporating the snatch lift into your training routine is essential. Not only does the snatch target multiple muscle groups simultaneously, but it also stimulates hypertrophy through specific mechanisms.
One of the primary ways the snatch promotes hypertrophy is by targeting the fast-twitch muscle fibers. These fibers are responsible for power and explosive movements, making them crucial for muscle growth. By performing the snatch lift, you engage these fibers, leading to hypertrophy and increased muscular strength.
Additionally, the snatch is a compound exercise that requires coordination and stability. As a result, it activates multiple muscle groups across your body, including the shoulders, back, legs, and core. The synergistic recruitment of these muscles during the lift stimulates hypertrophy across the entire body, ensuring balanced and comprehensive muscle development.
Furthermore, the snatch lift incorporates both eccentric and concentric muscle contractions. The eccentric phase, where the weight is lowered, causes muscular damage, which is a key stimulus for muscle growth. The subsequent concentric phase, where the weight is lifted explosively, promotes muscle fiber recruitment and further hypertrophy. This combination of eccentric and concentric contractions during the snatch allows for optimal hypertrophy stimulation.
By integrating the snatch lift into your training program and progressively increasing the weight and intensity over time, you can achieve significant muscle hypertrophy and power gains. It is important to focus on proper technique and gradually overload the muscles to continue challenging them for continued growth.
“The snatch lift’s ability to engage multiple muscle groups, target fast-twitch fibers, and incorporate eccentric and concentric contractions makes it an exceptional exercise for promoting hypertrophy and explosive power.”
To illustrate the muscle groups targeted by the snatch lift and its potential for hypertrophy enhancement, refer to the table below:
| Muscle Group | Hypertrophy Benefits of Snatch |
|---|---|
| Shoulders | Increases deltoid size and definition |
| Upper Back | Develops a strong and well-defined back |
| Legs | Builds quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes |
| Core | Enhances core stability and strength |
| Forearms and Grip | Strengthens grip and forearm muscles |
Perfecting Your Technique
When it comes to mastering the snatch lift, perfecting your technique is crucial. A solid understanding of the correct form and execution can not only improve your muscle activation but also optimize power generation. Let’s take a closer look at some essential tips and common mistakes to avoid.
1. Starting Position
Begin by standing with your feet hip-width apart and gripping the barbell with a snatch grip, hands positioned wider than shoulder-width apart. Keep your chest lifted, shoulders back, and core engaged.
2. First Pull
Initiate the lift by extending your legs, driving through your heels, and keeping the barbell close to your body. As you lift the bar, focus on keeping your arms straight and your back tight.
3. Transition
As the bar passes your knees, smoothly transition from the first pull into the second pull by aggressively extending your hips, knees, and ankles. This explosive movement generates power and allows the bar to accelerate upwards.
4. Catch Position
At the top of the lift, quickly drop into a squat position, guiding the bar overhead while keeping your arms locked. Maintain a stable core and an upright torso throughout this movement.
It’s important to note that perfecting your snatch technique takes time and practice. Don’t be discouraged if you don’t get it right away – focus on incremental improvements and listen to your body. Additionally, consider seeking guidance from a certified coach who can provide personalized feedback and technique corrections.
“Mastering the snatch technique is a journey of constant refinement. Stay patient, stay dedicated, and keep striving for progress.” – Coach Sarah Jackson
Optimizing your muscle activation and power generation during the snatch lift can lead to significant improvements in your overall performance. By focusing on proper technique, avoiding common mistakes, and seeking guidance when needed, you’ll be well on your way to mastering this challenging yet rewarding exercise.
Now, let’s move on to the next section and explore advanced variations of the snatch lift that can take your muscle development and power output to new heights.
Advanced Variations of the Snatch
As you continue to master the snatch lift, incorporating advanced variations can take your training to the next level. These variations not only challenge your muscles in new ways but also enhance power output, contributing to overall muscle development.
Variation 1: Hang Snatch
The hang snatch is an excellent variation that focuses on explosive power and coordination. Begin by holding the barbell in a standing position with a slight bend in your knees. Lower the barbell to just above knee level, maintaining a firm grip and upright posture. From this position, explosively extend your hips and knees, using the momentum to guide the barbell upwards. Catch it in an overhead position with your arms fully extended. This variation emphasizes power generation and enhances coordination between the lower and upper body.
Variation 2: Snatch Push Press
The snatch push press is a powerful variation that targets the muscles involved in the snatch lift while also developing shoulder strength and stability. Start with the barbell at shoulder level, holding it with a grip slightly wider than shoulder-width apart. Dip your knees, then explosively extend your hips and legs while simultaneously pressing the barbell overhead. Keep your core engaged and maintain control as you lower the barbell back to the starting position. This variation increases power output and trains the muscles to stabilize heavier loads.
Variation 3: Overhead Squat
The overhead squat variation is a challenging movement that demands excellent mobility, stability, and control. Begin by holding the barbell overhead with a wide grip. Slowly lower into a deep squat, keeping your chest upright and your core engaged. Focus on maintaining stability in the overhead position throughout the movement. The overhead squat variation not only targets the muscles involved in the snatch but also improves flexibility, mobility, and overall body awareness.
Variation 4: Snatch Balance
The snatch balance is a dynamic exercise that emphasizes speed, agility, and precision. Start with the barbell resting on your back in a back squat position. Dip your knees and explosively drive the barbell overhead, dropping into a deep squat as you catch the weight overhead. This variation improves your ability to quickly transition between the pulling and receiving phases of the snatch, enhancing power output and coordination.
Variation 5: Deficit Snatch
The deficit snatch is an advanced snatch variation that challenges your strength, power, and coordination. Perform the snatch lift while standing on an elevated surface, such as weight plates or a riser platform. This increased range of motion forces your muscles to work harder and adapt to heavier loads, leading to greater muscle development and power. Be sure to focus on maintaining proper form and technique as you perform this challenging variation.
| Variation | Description |
|---|---|
| Hang Snatch | A explosive variation that emphasizes power and coordination. |
| Snatch Push Press | A powerful variation that targets the muscles involved in the snatch while developing shoulder strength and stability. |
| Overhead Squat | A challenging movement that improves flexibility, mobility, and body awareness. |
| Snatch Balance | A dynamic exercise that improves speed, agility, and precision. |
| Deficit Snatch | An advanced variation that challenges strength, power, and coordination by performing the lift on an elevated surface. |
Experiment with these advanced snatch variations to keep your workouts fresh and continue challenging your muscles and power output. However, it is important to approach these variations with caution and ensure that you have mastered the basic snatch lift technique before attempting them. Always prioritize proper form and listen to your body to avoid injury and achieve optimal results.

Snatch and Jerk – Complementary Exercises
When it comes to maximizing muscle development and power generation, the snatch and jerk exercises are a dynamic duo that should not be overlooked. These two movements, when combined strategically, offer a comprehensive approach to strength training and can take your fitness journey to new heights.
The snatch and jerk exercises each target different muscle groups, making them ideal companions for a well-rounded workout routine. The snatch primarily focuses on the upper body, particularly the shoulders, upper back, and arms. On the other hand, the jerk is a lower body dominant movement that heavily engages the quads, glutes, and hamstrings.
By incorporating both the snatch and jerk exercises into your training program, you can reap the benefits of a full-body workout that targets all major muscle groups. This comprehensive approach not only ensures balanced muscle development but also enhances overall power and athletic performance.
Let’s take a closer look at the specific benefits offered by each exercise:
The Snatch Exercise:
| Benefits of the Snatch Exercise | Targeted Muscle Groups |
|---|---|
| Increases power output | Shoulders, upper back, arms |
| Promotes muscle hypertrophy | Improves athleticism and coordination |
| Enhances full-body strength and stability | – |
The Jerk Exercise:
| Benefits of the Jerk Exercise | Targeted Muscle Groups |
|---|---|
| Develops explosive lower body power | Quads, glutes, hamstrings |
| Improves core strength and stability | Engages the upper body as a stabilizer |
| Enhances overall athleticism | – |
As you can see, the snatch and jerk exercises offer unique benefits that complement each other perfectly. By incorporating both movements into your training routine, you can optimize muscle development, power output, and athletic performance.
Remember, proper form and technique are key to safely and effectively perform these exercises. If you are new to the snatch or the jerk, it is recommended to seek guidance from a qualified fitness professional to ensure correct execution and minimize the risk of injury.
Now that we understand how the snatch and jerk exercises complement each other, let’s explore more advanced variations of the snatch lift in the next section.
Progressive Overload in Snatch Training
When it comes to maximizing muscle growth and power development in snatch training, one key principle stands out: progressive overload. This concept involves gradually increasing the demands placed on your muscles to continually challenge them and stimulate further adaptation.
Progressive overload can be achieved in various ways during snatch training, allowing you to target different muscle groups and increase overall power output. Let’s explore some effective strategies that can help you implement progressive overload in your snatch workouts:
Varying Intensity
Incorporating different intensities into your snatch training routine is essential for progressive overload. This can be done by adjusting the weight you lift or the number of repetitions and sets you perform. Gradually increasing the load on the bar or the resistance in your snatch exercises will place greater demands on your muscles, leading to muscle growth and increased power.
Increasing Volume
Another way to apply progressive overload is by gradually increasing the volume of your snatch workouts. This can be done by adding more sets or repetitions to your training sessions over time. By increasing the total workload on your muscles, you create a stimulus for growth and power development.
Implementing Variation
Varying the snatch exercises you perform can also contribute to progressive overload. Incorporate different variations of the snatch, such as hang snatches or snatch pulls, into your training routine. These variations target specific muscle groups and challenge them in unique ways, promoting muscle growth and power improvement.
Remember, progressive overload should always be implemented gradually and in a controlled manner to avoid injury and overexertion.
To help you understand the importance of progressive overload in snatch training, take a look at the table below. It showcases the progressive overload principle applied to snatch workouts over a 12-week period, focusing on increasing intensity, volume, and variation:
| Week | Intensity | Volume | Variation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-4 | Increasing weight by 5-10% | Adding an additional set | Incorporating hang snatches |
| 5-8 | Increasing weight by 10-15% | Adding more repetitions | Incorporating snatch pulls |
| 9-12 | Increasing weight by 15-20% | Adding extra sets and repetitions | Incorporating deficit snatches |
Implementing progressive overload in your snatch training is crucial for continued muscle growth and power improvement. By gradually increasing the demands placed on your muscles through varying intensity, increasing volume, and implementing variation, you can ensure consistent progress and optimize your snatch workouts.
Proper Recovery and Injury Prevention
When incorporating the snatch lift into your training routine, it’s crucial to prioritize proper recovery and injury prevention strategies. By taking care of your body and implementing effective techniques, you can ensure long-term muscle gains and maintain overall well-being.
To maximize your snatch training results, make sure to:
- Rest and allow for recovery: Snatch exercises put a significant strain on your muscles and joints. Give yourself ample time to rest between training sessions to prevent overuse injuries and promote muscle repair and growth.
- Incorporate active recovery: Engaging in light exercises, such as swimming or yoga, on your rest days can improve blood circulation, reduce muscle soreness, and aid in the recovery process.
- Listen to your body: Pay close attention to any signs of discomfort or pain during your snatch training. If you experience sharp or persistent pain, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional to address the issue promptly.
- Warm-up properly: Prior to performing snatch lifts, engage in a thorough warm-up routine to increase blood flow, improve joint mobility, and enhance muscle activation. Incorporating dynamic stretches and light cardio exercises can also help reduce the risk of injury.
- Progress gradually: Avoid rushing to lift heavy weights or increase the intensity of your snatch training too quickly. Gradual progression allows your muscles and connective tissues to adapt and become stronger over time, minimizing the risk of injury.
- Ensure proper form: A proper snatch lift technique is crucial not only for maximizing muscle engagement but also for reducing the risk of strain or injury. Focus on maintaining good posture, keeping your movements controlled and precise, and seeking guidance from a qualified coach or trainer if needed.
In addition to recovery strategies, it’s important to implement injury prevention techniques to safeguard yourself during snatch training. Some key injury prevention tips include:
- Wearing appropriate lifting shoes to provide stability and support.
- Using weightlifting belts or wraps to protect your lower back and promote proper spinal alignment.
- Practicing good nutrition and hydration to support muscle recovery and reduce the risk of muscle imbalances.
- Incorporating exercises that target mobility and flexibility, such as foam rolling and stretching, to improve joint range of motion and prevent muscle imbalances.
- Gradually introducing snatch variations and complex movements to prevent overload and allow for progressive adaptation.
- Listening to your body and adjusting your training intensity or technique if you feel any discomfort or pain.
“Recovery and injury prevention are essential components of any training program, including snatch lifting. Taking the necessary steps to rest, recover, and prevent injuries will not only protect your body but also ensure consistent progress and long-term muscle gains.”
The Importance of Rest and Recovery
Rest and recovery play a critical role in optimizing snatch training results. During periods of rest, your muscles repair damaged tissue, replenish energy stores, and grow stronger. Neglecting to prioritize recovery can lead to overtraining, increased injury risk, and hindered muscle growth.
By implementing proper recovery and injury prevention strategies, you can continue to push your limits in snatch training while minimizing the risk of setbacks and improving overall performance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the snatch lift is a highly effective exercise for building muscle and enhancing power in the upper body. When performed with proper technique, it engages multiple muscle groups, including the shoulders, back, hips, and legs, resulting in overall strength and power development.
By incorporating variations of the snatch lift, such as the hang snatch or power snatch, you can further challenge your muscles and stimulate greater muscle hypertrophy. These variations target different parts of the muscle fibers, ensuring a well-rounded development and maximizing your potential gains.
The snatch lift not only improves muscle strength and size but also has significant benefits for athletic performance. The explosive nature of the lift enhances power output, translating to improved performance in sports such as weightlifting, sprinting, and jumping. Additionally, the snatch lift trains the body to generate power from the hips, promoting better coordination and agility.
Whether you are an athlete looking to enhance your performance or an individual seeking to improve overall strength and muscle development, incorporating the snatch lift into your training regimen can yield significant benefits. Remember to prioritize proper technique, gradually increase the weight lifted, and allow for adequate recovery to prevent injuries and optimize your results.
FAQ
What is the snatch lift?
The snatch lift is a weightlifting exercise that involves lifting a barbell from the floor to an overhead position in one smooth motion. It primarily targets the muscles in the upper body, including the shoulders, back, and arms.
How does the snatch lift build muscle?
The snatch lift is a highly demanding compound movement that recruits multiple muscle groups, stimulating muscle growth and development. By incorporating the snatch lift into your training routine, you can effectively target and strengthen your upper body muscles, leading to improved muscle hypertrophy over time.
Can split squats be integrated with the snatch lift?
Yes, split squats can be integrated with the snatch lift to further enhance muscle development and power in the lower body. By incorporating split squats, you engage the muscles in the legs, particularly the quads and glutes, which can contribute to improved overall strength and stability during the snatch lift.
How can the snatch lift promote hypertrophy?
The snatch lift promotes hypertrophy, or muscle growth, through a combination of factors. The explosive nature of the lift recruits a high number of muscle fibers, leading to microtears in the muscle tissue. These microtears, when repaired through proper nutrition and rest, result in muscle growth and increased hypertrophy over time.
What are some tips for perfecting snatch lift technique?
To perfect snatch lift technique, it is essential to focus on proper form and execution. Some tips include maintaining a strong and stable core, initiating the lift with a powerful hip drive, and keeping the bar close to the body throughout the movement. Practicing with lighter weights and seeking guidance from a qualified coach can also help refine your technique.
Are there advanced variations of the snatch lift?
Yes, there are advanced variations of the snatch lift that can be incorporated to further challenge your muscles and enhance power output. These variations include the hang snatch, snatch balance, and snatch pull, each targeting specific muscle groups and placing different emphasis on power generation.
How do the snatch and jerk exercises complement each other?
The snatch and jerk exercises complement each other by targeting different muscle groups and movement patterns. While the snatch primarily focuses on explosiveness and power in the upper body, the jerk emphasizes the lower body and overhead stability. By incorporating both exercises into your training routine, you can achieve a more balanced and well-rounded development of muscle and power.
What is progressive overload in snatch training?
Progressive overload refers to the gradual increase in intensity, volume, or difficulty of a training stimulus over time. In snatch training, it involves progressively challenging your muscles by increasing the weight lifted, the number of repetitions, or the complexity of the lift. This method stimulates continued muscle growth and power improvement, preventing plateaus in your fitness journey.
Why is proper recovery and injury prevention important in snatch training?
Proper recovery and injury prevention strategies are crucial in snatch training to ensure long-term muscle gains and overall wellbeing. The snatch lift is a demanding exercise that places significant stress on the body. By allowing adequate rest and recovery between sessions, prioritizing mobility work, and addressing muscle imbalances, you can reduce the risk of injuries and optimize your performance in the snatch lift.
Effective Shoulder Calisthenics for Strength & Flexibility
Welcome to my comprehensive guide on effective shoulder calisthenics! As a fitness enthusiast, I understand the importance of having strong and flexible shoulder muscles. They not only improve upper body workouts but also enhance daily activities like lifting and carrying. In this guide, I will share a variety of bodyweight shoulder exercises that can be done at home or in the gym to improve your shoulder strength and flexibility. These exercises will target the muscles in your shoulders, helping you achieve optimal performance.
Key Takeaways:
- Shoulder calisthenics exercises target shoulder muscles for strength & flexibility
- These bodyweight exercises can be done at home or in the gym
- Having stronger and flexible shoulders enhances upper body workouts and daily activities
- Improving shoulder mobility is crucial for overall shoulder health
- Rotator cuff muscles are essential for shoulder strength and stability
Shoulder Calisthenics: The Basics
As I mentioned earlier, shoulder calisthenics can greatly benefit your shoulder strength and flexibility. Before we dive into specific exercises, let’s cover the basics of shoulder calisthenics.
The Importance of Shoulder Exercises
The shoulders are a crucial component of the upper body and play a significant role in overall body movement and posture. By incorporating shoulder exercises into your workout routine, you can improve your upper body strength, stability, and range of motion.
The Benefits of Bodyweight Shoulder Exercises
Bodyweight shoulder exercises are a highly effective way to target the muscles in your shoulders without equipment. They are perfect for beginners, but also offer a challenge for advanced athletes. Plus, they can be done anywhere, anytime, making it easy to fit them into your daily routine.
How Strength Training Can Enhance Your Shoulder Muscles
Strength training, including bodyweight exercises and weightlifting, is essential for building strong and powerful shoulders. It can help increase muscle mass, improve bone density, and enhance overall physical fitness. By incorporating strength training into your shoulder calisthenics routine, you can achieve optimal results.
“The shoulders are a crucial component of the upper body and play a significant role in overall body movement and posture.”
Shoulder Mobility Exercises
Having good shoulder mobility is essential for overall shoulder health and injury prevention. In this section, I will share with you effective shoulder mobility exercises that can promote flexibility, reduce stiffness, and enhance your range of motion.
Some of the best shoulder mobility exercises include:
- Arm Circles: Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart, extend your arms out to the sides, and make circles with your arms.
- Shoulder Rolls: Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and roll your shoulders forwards and backwards.
- Wall Angels: Stand with your back against a wall and move your arms up and down to touch the wall.
- Doorway Stretch: Stand in a doorway and place your hands on the door frame, then gently lean forward until you feel a stretch in your chest and shoulders.
These exercises can be performed as part of your warm-up routine or as a standalone mobility workout. Incorporating them into your routine can help improve your shoulder health, mobility, and performance.
Shoulder Stability Exercises
Maintaining strong and stable shoulders is essential for your overall well-being, as it allows you to perform daily activities with ease and engage in sports activities without the fear of injuries. In this section, I will introduce you to a variety of shoulder stability exercises that focus on strengthening the muscles responsible for providing support and stability to your shoulders.
Before diving into the exercises, it is important to note that proper form and technique are crucial to achieving optimal results and preventing injuries. Therefore, it is recommended that you start with lighter weights and gradually increase the difficulty as you build your shoulder strength and stability.
Exercise 1: Shoulder External Rotation
| Steps | Common Mistakes |
|---|---|
|
|
This exercise targets the rotator cuff muscles, which are crucial for shoulder stability. It also helps correct any muscle imbalances that may lead to shoulder injuries.
Exercise 2: Plank with Shoulder Taps
| Steps | Common Mistakes |
|---|---|
|
|
This exercise strengthens your shoulders and your entire core, which can help prevent shoulder injuries and improve overall upper body strength.
Exercise 3: Seated Dumbbell Cuban Press
| Steps | Common Mistakes |
|---|---|
|
|
This exercise targets the rotator cuff muscles and the muscles in your upper back, which are essential for shoulder stability and posture.
Incorporating these exercises into your shoulder routine can help you achieve optimal shoulder stability and prevent injuries. Remember, consistency and proper technique are key to achieving your fitness goals.
Strengthening the Rotator Cuff
As I mentioned earlier, the rotator cuff muscles are key players in shoulder strength and stability. In this section, let’s delve deeper into specific exercises that can help enhance the strength and stability of your rotator cuff muscles.
Firstly, external rotations are a fantastic exercise to isolate the rotator cuff muscles. To perform this exercise, stand with your elbows at a 90-degree angle and hold a lightweight dumbbell in each hand. Keeping your elbows glued to your sides, rotate your forearms outward, moving the dumbbells away from the body. Slowly bring the dumbbells back to the starting position, completing one repetition. Aim for three sets of eight to ten repetitions.
The next exercise involves the use of resistance bands. Stand with one end of a resistance band attached to a fixed object and the other end held in your hand. Keep your elbows bent at a 90-degree angle, with your upper arms positioned parallel to the floor. Pull the resistance band outward, away from your body, feeling the resistance in your shoulders and upper arms. Slowly bring the resistance band back to start, completing one repetition. Aim for three sets of eight to ten repetitions.
Finally, the prone horizontal abduction exercise targets the muscles of the posterior rotator cuff. Lie face down on a mat with your arms extended out to the sides, making a T-shape with your body. With your hands slightly above the level of your shoulders, engage your back muscles and lift your arms off the floor until they are in line with your body. Hold for a few seconds, then release back to the starting position. Aim for three sets of eight to ten repetitions.
These exercises, when performed regularly, can help improve the strength and stability of your rotator cuff muscles, reducing the risk of shoulder injuries and enhancing your upper body workouts.
Advanced Shoulder Calisthenics
If you’ve been consistently practicing shoulder exercises and are ready for a challenge, it’s time to give advanced shoulder calisthenics a try. These exercises require a higher level of strength and stability and can help you progress further in your shoulder calisthenics journey.
One of the most challenging bodyweight shoulder exercises is the Handstand Push-Up. This move targets your entire shoulder complex while also engaging your core and improving your balance. Start by practicing against a wall before attempting it freestanding.
Another challenging exercise to try is the Ring Dip, which targets your chest, triceps, and shoulders. Using gymnastic rings instead of static bars will increase the difficulty due to the need to stabilize your body throughout the movement.
If you’re looking for a full-body challenge, the Burpee Pull-Up is a great option. This exercise engages your shoulders, back, arms, and core, all while getting your heart rate up. Start by practicing the pull-up and burpee separately before attempting the full movement.
Remember to always prioritize proper form and technique over the number of reps or sets you are doing. It’s better to perform fewer reps with perfect form than to do more with improper form and risk injury. Always listen to your body and progress at a pace that works for you.
Creating an Effective Shoulder Routine
When it comes to achieving strong and healthy shoulders, creating an effective routine is key. By combining different shoulder exercises, you can target all the muscles in your shoulders and upper body, optimizing your workouts for the best possible results.
When building your shoulder routine, consider incorporating exercises from each of the following categories:
Shoulder Mobility Exercises
These exercises help improve the range of motion in your shoulders, reducing stiffness and preventing injuries. Some examples include:
| Exercise | Description |
|---|---|
| Shoulder circles | Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and your arms by your sides. Slowly lift your shoulders up towards your ears, then back and down in a circular motion. |
| Thread the needle stretch | Start on all fours, with your hands and knees on the ground. Lift your right arm up towards the ceiling, then thread it through the space between your left arm and left leg. Hold for a few seconds, then switch sides. |
Shoulder Stability Exercises
These exercises help strengthen the muscles responsible for stabilizing your shoulders, preventing injuries and improving overall shoulder strength. Some examples include:
| Exercise | Description |
|---|---|
| Shoulder taps | Start in a plank position, with your hands directly below your shoulders. Lift your right hand off the ground and tap your left shoulder, then switch sides. |
| Wall angels | Stand with your back against a wall and your hands at your sides. Slowly raise your arms up, keeping them against the wall, forming a “W” shape. Lower your arms back down and repeat. |
Rotator Cuff Exercises
These exercises specifically target the rotator cuff muscles, which play a significant role in shoulder stability and strength. By strengthening these muscles, you can reduce the risk of shoulder injuries and enhance overall shoulder performance. Some examples include:
| Exercise | Description |
|---|---|
| Side-lying external rotation | Lie on your side with your elbow bent to 90 degrees and your forearm resting on the ground. Slowly rotate your arm outwards, keeping your elbow against your side. Return to starting position and repeat on the opposite side. |
| Prone horizontal abduction | Lie on your stomach with your arms extended out in front of you. Slowly lift your arms up towards the ceiling, keeping them straight and squeezing your shoulder blades together. Lower your arms back down and repeat. |
Remember to take proper rest periods between sets and gradually increase the number of reps and sets to avoid overtraining.

With these exercises in mind, you can create a well-rounded shoulder routine that will help you achieve optimal results. Incorporate them into your upper body workouts to enhance your overall strength and flexibility, and enjoy the benefits of a strong and healthy upper body.
Injury Prevention and Safety Tips
As with any physical activity, it’s important to prioritize safety when performing shoulder exercises or workouts. Here are some tips to reduce the risk of shoulder injuries:
- Start with a proper warm-up: Before starting any exercises, be sure to warm up your shoulders and upper body with some light cardio or dynamic stretches. This will prepare your muscles for the workout and help prevent injury.
- Use proper form: When performing shoulder exercises, use proper form to avoid straining your shoulders or other muscles. If you’re not sure about proper form, seek guidance from a certified personal trainer or physical therapist.
- Gradually increase weight and intensity: Don’t jump into heavy weights or high-intensity exercises right away. Gradually increase weight and intensity to ensure proper muscle development and avoid injury.
- Listen to your body: Pay attention to how your shoulders feel during workouts. If you experience pain or discomfort, stop the exercise and talk to a healthcare professional.
- Take breaks and rest days: Don’t overwork your shoulders. Take breaks between exercises and rest days between workouts to allow your muscles to recover and prevent strain or injury.
- Stay hydrated: Proper hydration is essential for optimal muscle function and injury prevention. Drink plenty of water before, during, and after your workouts.
By following these injury prevention tips and safety guidelines, you can enjoy a safe and effective shoulder exercise routine.
Incorporate shoulder exercises and workouts into your regular fitness routine, and enjoy the benefits of stronger, healthier shoulders. Remember to prioritize safety and proper form to avoid injury and achieve optimal results.
Incorporating Shoulder Calisthenics into Your Fitness Routine
Now that you have learned various shoulder calisthenics exercises, it’s time to incorporate them into your existing fitness routine to achieve stronger, healthier shoulders. Here are some helpful tips and suggestions:
Dedicate a Shoulder Day
If you want to focus solely on your shoulders, consider dedicating a specific day to shoulder workouts. This can be an effective way to ensure that you give your shoulder muscles the attention and time they need to grow and improve. Here’s an example of a typical shoulder workout:
| Exercise | Sets x Reps |
|---|---|
| Shoulder Press | 3 x 10 |
| Lateral Raise | 3 x 12 |
| Bent-Over Rear Delt Fly | 3 x 12 |
| Arnold Press | 3 x 10 |
| Upright Row | 3 x 12 |
Incorporate Shoulder Exercises into Full-Body Workouts
If you prefer full-body workouts, you can still include shoulder exercises in your routine. Here’s an example of a full-body workout that incorporates shoulder exercises:
- Push-ups: 3 sets x 12 reps
- Chin-ups: 3 sets x 8 reps
- Squats: 3 sets x 10 reps
- Bent-Over Rows: 3 sets x 12 reps
- Lateral Raise: 3 sets x 12 reps
- Plank: 3 sets of 1 minute
- Shoulder Press: 3 sets x 10 reps
Remember to always prioritize proper form and technique when performing shoulder exercises. Gradually increase the intensity and volume of your workouts to avoid injury and improve your shoulder strength and stability over time.
Tip: It’s important to give your muscles time to recover between workouts, so avoid overtraining your shoulders by limiting your exercises to two to three times per week.
Conclusion
Incorporating shoulder calisthenics exercises into your training routine is an effective way to improve your shoulder strength and flexibility. Through this comprehensive guide, I have shared a variety of exercises that target the different muscles in your shoulders and upper body.
By starting with the basics of shoulder calisthenics and progressing to more advanced exercises, you can build a well-rounded shoulder routine that helps reduce the risk of injury, improves overall shoulder performance, and enhances your upper body workouts. Additionally, by following injury prevention tips and safety guidelines, you can ensure a safe and effective training experience.
Remember, whether your goal is to increase shoulder mobility, stabilize your shoulders, or strengthen your rotator cuff muscles, consistency and proper form are key. By following the exercises and recommendations outlined in this guide, you can achieve stronger, healthier shoulders and take your shoulder calisthenics to the next level. So, don’t hesitate to add these exercises to your fitness routine and see the difference they can make.
FAQ
What are some effective shoulder calisthenics exercises?
Some effective shoulder calisthenics exercises include push-ups, handstand push-ups, pike push-ups, shoulder taps, and dips.
How often should I do shoulder calisthenics exercises?
It is recommended to perform shoulder calisthenics exercises 2-3 times per week, allowing at least one day of rest in between each session to allow for recovery and muscle growth.
How can shoulder exercises benefit my upper body workouts?
Shoulder exercises help strengthen the muscles in your upper body, including the deltoids, trapezius, and triceps. This can improve your overall upper body strength and enhance performance in exercises such as bench presses, pull-ups, and overhead presses.
What are some bodyweight shoulder exercises?
Some bodyweight shoulder exercises include push-ups, pike push-ups, wall walks, handstand holds, and shoulder taps.
How can shoulder strength training improve my shoulder stability?
Shoulder strength training exercises target the muscles responsible for stabilizing the shoulder joint, such as the rotator cuff muscles. By strengthening these muscles, you can improve shoulder stability, reduce the risk of injuries, and enhance overall shoulder function.
What are some shoulder mobility exercises?
Some shoulder mobility exercises include shoulder circles, arm circles, shoulder dislocations with a resistance band, and wall slides.
How can shoulder workouts improve shoulder flexibility?
Shoulder workouts, especially those that incorporate dynamic stretching exercises, can help improve shoulder flexibility by increasing the range of motion in the shoulder joint and reducing stiffness in the muscles surrounding the shoulders.
What are some calisthenics exercises specifically for shoulders?
Some calisthenics exercises specifically for shoulders include handstand push-ups, pike push-ups, archer push-ups, and suspended push-ups using gymnastic rings.
How do I create a shoulder routine?
To create a shoulder routine, choose a combination of exercises that target different areas of the shoulders, such as deltoids, rotator cuff, and traps. Start with compound exercises and progress to isolation exercises, ensuring proper form and gradually increasing intensity.
Are there any safety tips I should follow when performing shoulder exercises?
Yes, some safety tips include using proper form and technique, not overloading or straining the shoulders, warming up adequately before the workout, and listening to your body’s signals to avoid pushing beyond your limits.
How can I prevent shoulder injuries while performing shoulder exercises?
To prevent shoulder injuries, it’s important to start with lighter weights and progress gradually, focus on proper form and technique, avoid excessive repetitive movements, and incorporate sufficient rest and recovery days into your training routine.
How can I incorporate shoulder calisthenics exercises into my existing fitness routine?
You can incorporate shoulder calisthenics exercises by dedicating a specific day to shoulder training or by including them in your full-body workouts. It’s important to strike a balance between targeting your shoulders adequately and allowing sufficient recovery time for optimal muscle growth and development.









